Grinding wheels have three key points and five main factors.
Three major elements: abrasive grains, bonding agent, and pores.
Five characteristics: abrasive grain material, abrasive grain size, abrasive grain density, binder characteristics, and binder hardness.
This article will focus on bonding agents.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Bonding agents in grinding tools bind abrasive particles together, helping the tool maintain its shape, strength, and hardness throughout use.
During grinding, abrasive grains supported by the bond cut into the workpiece. When grains become dull, they break or detach, maintaining good grinding performance. Therefore, the bond choice significantly impacts the tool’s hardness, wear resistance, and toughness.
Note: the evaluation standard here compares bonds under the same abrasive conditions.
Bond Performance Classification
Inorganic grinding tools: ceramic bond, metal bond, electroforming bond, etc.
Organic Abrasives: These use binders like resin and rubber.
Resin Bond

Symbolized as “R”
Resin bonds are based on synthetic or natural resin and commonly used in grinding wheels and tools.
Resin’s high toughness and flexibility allow for efficient grinding and adaptability.
Resin bonds’ properties make them widely used in various processes, especially where rapid cutting and rough grinding are needed.
Advantages of Bond
High Toughness: Resin-bonded abrasives can absorb impacts during grinding, reducing the risk of material damage.
High Elasticity: Resin binders offer a smoother grinding process by minimizing vibrations, helping to maintain surface quality.
Good Wear Resistance: While not as durable as ceramic binders, resin binders offer adequate wear resistance for high-speed applications.
Good Cutting Ability: Suitable for high-speed operations, particularly effective for cutting and rough grinding where rapid material removal is needed.
High Bond Strength: Resin binders have a higher adhesive strength than ceramic binders, making them ideal for high-speed grinding applications.
Capability for Complex Shapes: With low curing temperatures and minimal shrinkage, resin binders can be shaped into complex and specialized abrasive tools.
Disadvantages of Bond
Poor Water Resistance: Resin can degrade, soften, or lose effectiveness when in prolonged contact with water or other liquids.
Limited Heat Resistance: Resin binders are not ideal for long-term grinding in high-temperature environments, although they are less likely to cause grinding burns.
General Bond Types
Phenolic Resin: The most commonly used resin binder, moderately priced with reliable performance and moderate heat resistance, suitable for general grinding tasks.
Epoxy Resin: Known for its chemical resistance and strong bonding ability, making it suitable for grinding operations requiring higher environmental durability.
Scope of Application
Metal Processing: Ideal for cutting and rough processing of materials like high-speed steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
Wood Processing: Resin wheels are often used for polishing and finishing wood and plastic surfaces.
High-Precision Grinding: Some resin-bonded abrasives can be used for high-precision grinding applications, such as for fine grinding of precision ceramics and glass.
High-Speed Cutting: With wear resistance and flexibility, resin binders are suitable for high-speed grinding wheels used in cutting and fast grinding applications.
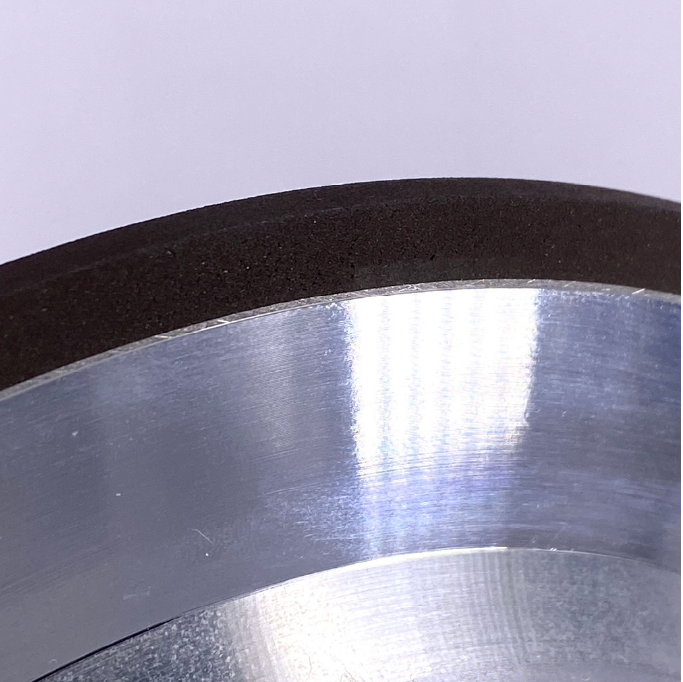
Vitrified
Symbolized as “V”
Ceramic bonding agents primarily consist of clay, feldspar, and quartz, with secondary components like talc, borax, and borosilicate. Sintered at 1200°C, these materials form a hard structure. Since they use vitreous bonding, they are porous, endowing grinding tools with excellent hardness and wear resistance.
Advantages of Bond
High Hardness and Wear Resistance: Ceramic-bonded abrasives generally have very high hardness, making them highly effective for grinding hard materials such as steel, hard alloys, and ceramics.
Excellent Heat Resistance: Ceramic bonds can withstand high temperatures without deforming or degrading, making them suitable for high-speed grinding and applications in high-heat environments.
Good Shape Retention: Ceramic-bonded abrasives maintain their shape and are resistant to wear and deformation, which is crucial in precision machining for maintaining high accuracy.
Disadvantages of Bond
Low Thermal Expansion: This minimizes dimensional changes, allowing for smoother and more precise grinding processes.
Poor Resistance to Rapid Temperature Changes: Rapid cooling and heating can cause internal stresses due to differences in thermal expansion, leading to cracks or fractures.
Scope of Application
Precision Grinding: Ceramic-bonded abrasives are widely used for precision grinding of tools, molds, and machine parts, particularly excelling in the production of gears, bearings, and optical lenses.
Hard Material Grinding: Ideal for grinding high-hardness materials like stainless steel, hard alloys, ceramics, and glass, ceramic bonds provide stable cutting force over prolonged processing.
High-Speed Grinding: Ceramic wheels are suited for high-speed grinding, particularly in high-efficiency, high-volume production, such as high-speed grinding of steel and iron in metalworking applications.
Metal Bond
Symbolized as “M”
Metal-bonded abrasives primarily consist of bronze-bonded and electroplated types. Bronze-bonded abrasives are made by mixing copper powder, tin powder, and other materials to improve performance, which are then blended with abrasive grains and formed under pressure before sintering.
Advantages of Bond
High Strength and Durability: Metal-bonded abrasives exhibit extremely high strength, capable of withstanding intense grinding pressure and high-temperature environments, allowing them to maintain stable shape and performance under heavy loads.
Good shape retention: Metal-bonded abrasive tools have excellent abrasive retention and are not easy to wear or deform. This is particularly important in precision machining and can maintain high-precision machining effects.
Heat Resistance: Metal bonds withstand high temperatures, making them effective in high-speed grinding and applications involving extensive heat treatment, without decomposing or softening like organic bonds.
Excellent Thermal Conductivity: The high thermal conductivity of metals allows for efficient heat dissipation, preventing the abrasive from overheating, thereby extending tool life and enhancing the surface quality of the workpiece.
Wear Resistance: Metal-bonded abrasives offer superior wear resistance, especially in long-term heavy-load operations, reducing the wear rate and extending tool life, minimizing replacement frequency.
Precision Grinding Capability: Metal-bonded abrasives maintain high grinding precision, making them ideal for applications requiring extreme accuracy, such as in optical devices and precision mechanical parts.
Suitability for High-Hardness Materials: These abrasives are well-suited for processing high-hardness materials, such as hard alloys, ceramics, glass, and ultra-hard materials like diamond and cubic boron nitride (CBN), maintaining grinding efficiency and precision under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
Disadvantages of Bond
Brittleness: Although bronze bonds have moderate hardness, they are relatively brittle compared to metals like nickel or steel. Bronze-bonded abrasives may crack or break under heavy grinding loads or intense vibration, making them less suitable for high-stress environments.
Scope of Application
Ceramic, Glass, and Stone Processing: Metal-bonded abrasives provide effective cutting power and extended service life when processing hard, brittle materials like ceramics, glass, and stone, producing a better surface quality than traditional wheels.
Silicon Carbide and Silicon Nitride Processing: These special ceramics are difficult to process, but metal-bonded abrasives enable precise grinding.
Semiconductor Wafer Processing: Metal-bonded grinding wheels are used for cutting and grinding semiconductor wafers, a process requiring high precision and material integrity. Metal bonds ensure consistent cutting force and controlled surface roughness.
Electroplated
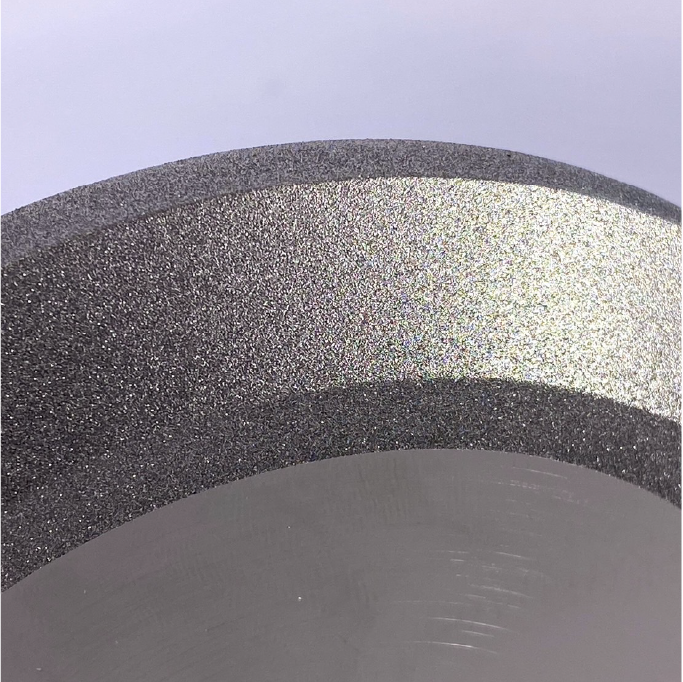

Symbolized as “P”
Electroforming bond is a type of bond that utilizes electroplating technology to fix the abrasive onto the bench metal, usually using a metal such as nickel or copper as the bonding agent.
Electroforming bond is a kind of bonding agent with high bonding strength, generally single or multi-layer abrasive grains are plated on metal table gold by electroplating method, and this kind of abrasives is mainly used for processing of super-hard materials, especially diamond or boron nitride (CBN) abrasives.
Electroforming bonded grinding tools are well known for their high precision and grinding performance, and are commonly used in high speed, high precision grinding.
Advantages of Bond
High Grinding Efficiency: Electroplated bonded abrasives offer high grinding efficiency, as the abrasive grains are largely exposed without excessive bonding material, making them especially effective in processing hard and brittle materials like ceramics, glass, and tungsten carbide.
Good heat dissipation: The metal layer of the electroforming compound is very thin, so the heat generated during grinding can be dissipated more easily, thus reducing the heat damage to the grinding tool and workpiece, especially when grinding at high speed.
Good shape retention: Electroforming bonded abrasives have a strong shape retention capability and are able to maintain their accuracy over a long period of time, which makes them very popular in applications requiring high precision.
Can produce complex abrasives with shapes: Electroforming fluid has high mobility during the process, which can penetrate into the small grooves and crevices on the surface of the abrasives and cover the areas that are difficult to be processed, which makes it suitable for the production of abrasives with shaped and complex structures.
Wide Application Range: Electroplated bonded abrasives are versatile and can be used to grind various high-hardness materials, including metals, ceramics, glass, and other challenging materials, particularly in high-precision and high-efficiency grinding and cutting applications.
Disadvantages of Bond
Poor durability: Electroforming bonded abrasives usually have only one layer of abrasive, once this layer is worn out, the performance of the abrasive will drop dramatically and it can not be used any more, so it has a relatively short service life.
Difficulty in reconditioning: Electroforming bonded abrasives are not easy to recondition after wear, and often need to be replaced with new abrasives or re-plated, which can be costly in some high-volume production applications.
Higher Manufacturing Costs: The manufacturing process of electroforming bonded abrasives is relatively complex and requires precise control, resulting in higher manufacturing costs.
Scope of Application
Processing of super-hard materials: Electroforming bonded abrasives are commonly used in the manufacture of diamond and CBN abrasives, which are suitable for grinding super-hard materials such as tungsten carbide, stainless steel, ceramics and glass.
Precision Machining: Ideal for high-precision tasks, such as mold making, precision tool manufacturing, and optical glass cutting and grinding.
High-Efficiency Grinding: Employed in high-efficiency grinding applications, such as automotive and aerospace component manufacturing, providing excellent efficiency and accuracy in high-speed grinding.
Special Shape Grinding Tools: Since electroforming bonded grinding tools can be made into special shapes according to the requirements, they are often used for grinding tools that require complex geometries, such as small hole processing tools and special shaped grinding tools.
Conclusion
Binding agent is a key material in the manufacture of abrasives, which directly affects the performance, application range and service life of abrasives. According to different processing requirements and material properties, there are many types of binders, the most common of which include metal binders, ceramic binders, resin binders and electroforming binders. Each type of bond has its own specific advantages and limitations and is suitable for different grinding applications. When selecting a bond, the advantages and disadvantages of these materials are weighed against the requirements.
Metal binders are usually chosen for high-strength, heavy-duty grinding processes.
For applications that require high precision or are heat sensitive, ceramic or resin binders may be more suitable.
In addition, cost, hardness of the material to be processed, cooling conditions and environmental factors are also important considerations when selecting a bond.
The correct choice of abrasive bond is the key to ensuring process efficiency, finished product quality and economic efficiency. In the ever-evolving modern manufacturing industry, advances in binder technology have also led to improvements in the performance of abrasives, enabling them to cope with increasingly complex and demanding industrial applications.
Action
- How to choose grinding wheel>>>How to Choose Between Diamond Wheels and CBN Wheels?
- The basic knowledge of abrasives that must be known>>>Grinding-Abrasive Introduction
- Whether the current measured surface roughness meets your expected goals>>>Comparison Chart of Grinding Polishing and Surface Roughness
- Is the current grinding wheel wear normally>>>What is the current state of grinding wheels? -Electroforming Wheels
- Action>>>Diamond and CBN grinding wheel, Polishing abrasive, Polishing Equipment, Polishing Tools
- Review
We offer customized adjustments to the grinding process, tailored to meet processing requirements for maximum efficiency.
After reading the content, if you still don’t know how to select the most suitable option,
Feel free to contact us and we will have specialist available to answer your questions.
If you need customized quotations, you’re also welcome to contact us.
Customer Service Hours: Monday to Friday 09:00~18:00 (GMT+8)
Phone: +8867 223 1058
If you have a subject that you want to know or a phone call that is not clear, you are welcome to send a private message to Facebook~~
Honway Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/honwaygroup

