As an indispensable tool in machining, the performance and condition of the grinding wheel have a huge impact on the processing efficiency and quality.
During the grinding process, the structure of the grinding wheel, the abrasive grain characteristics, the grinding pattern and the shape of the abrasive chips generated will all change with the machining conditions, which in turn will affect the cutting effect and the surface finish of the workpiece.
This article discusses the characteristics of grinding wheels and the dynamic changes in the grinding process, which not only helps to understand the nature of grinding phenomena, but also provides a theoretical basis for machining parameters and improving machining quality. In this paper, the structure of the grinding wheel, the mechanism of abrasive action, the grinding state and the abrasive debris morphology will be analyzed
Table of Contents
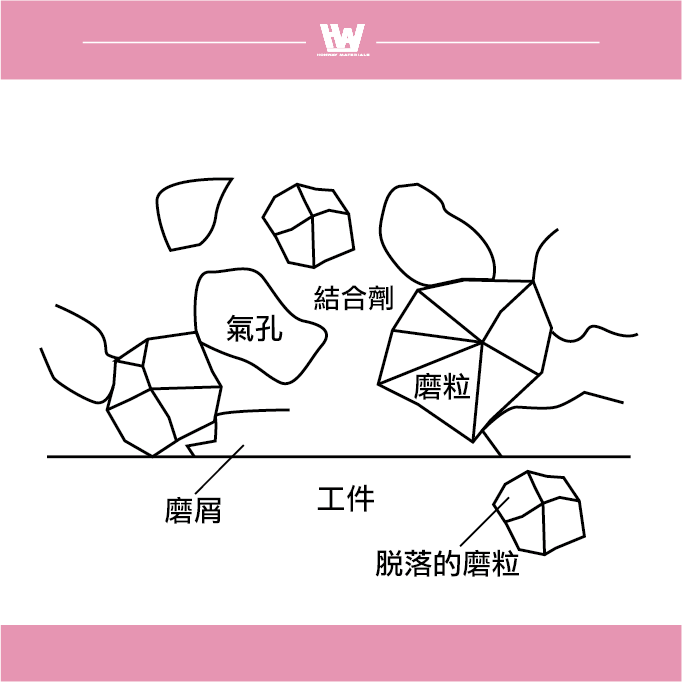
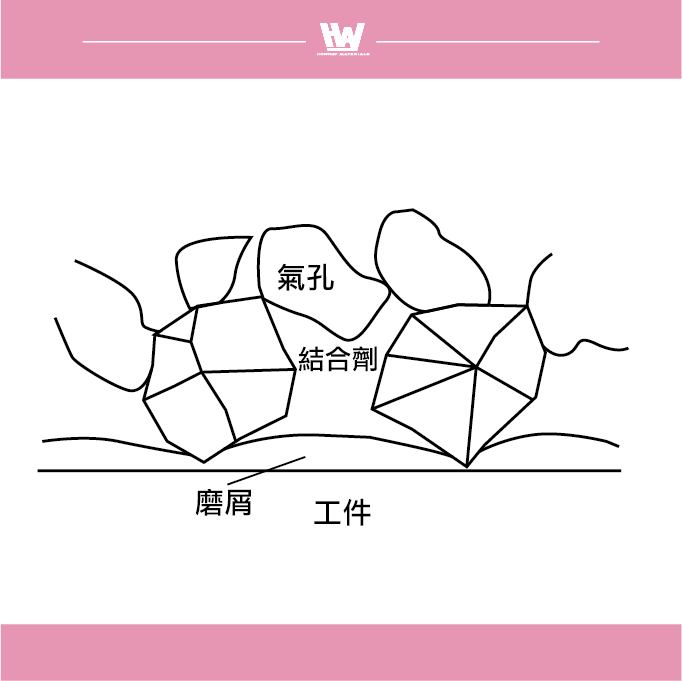
The structure of the grinding wheel
Grinding wheel: The shape of the grinding wheel is mainly round, and it is usually designed with an internal hole for easy installation on the grinder. In addition to the standard round shape, grinding wheels are available in a variety of shapes, such as flat, cup, and dish.
- Flat grinding wheels are suitable for surface grinding over large areas.
- Cup-shaped grinding wheels are often used for in-house or special-shaped machining.
- Pointed grinding wheels, on the other hand, are designed for delicate workpieces and can be used in tight spaces for grinding.
Abrasive grains: In the grinding operation, each abrasive grain on the surface of the grinding wheel is sharpened from the workpiece with a sharp cutting edge. Abrasive grains come in a variety of shapes and may be sharp, flat, or other shapes.
Abrasive properties
Cutting capacity: The sharpness of the abrasive grain directly affects its cutting ability, and the sharp abrasive grain can cut the workpiece material more effectively.
Bevel vs. Negative Bevel: The bevel angle of the abrasive grain affects the cutting force and the flow of chips during the cutting process, and the abrasive grain with a negative bevel angle can reduce the cutting resistance.
Granularity: The particle size of the abrasive grain will affect the finish of the surface of the workpiece, and finer abrasive grains usually achieve a better finish.
Four modes of action of abrasive grains on the workpiece
Usually the amount of abrasive cutting edge is 1um or less, even if the cutting edge is in contact with cutting, it may not discharge abrasive chips, depending on the shape of the cutting edge, the size of the cutting amount, the nature of the workpiece, and the cutting speed, which are mainly divided into four cutting types: (1) friction (2) plastic deformation (3) excavation (4) cutting
1. Friction
Features: The contact between the abrasive particles and the surface of the workpiece is mainly rubbing, and the discharge of abrasive chips is very limited.
Influencing factors: When the plunge amount is small and the cutting speed is low, the friction pattern is more obvious.
2. Plastic deformation
Features: The workpiece material is plastically deformed under the action of abrasive particles, and there may not be obvious abrasive debris.
Influencing factors: The hardness and toughness of the material will affect the degree of plastic deformation.
3. Dig up
Features: Abrasive grainsDuring the cutting process, the workpiece material is picked up to form small flakes of abrasive chips.
Influencing factors: When the amount of cutting is moderate, the excavation pattern will be more obvious, and it is related to the shape of the abrasive grain.
4. cutting
Features: Abrasive grains cut the workpiece material directly with a sharp cutting edge, producing visible abrasive chips.
Influencing factors: When the cutting amount is large and the cutting speed is high, the cutting type is the main type, which can effectively remove the material.
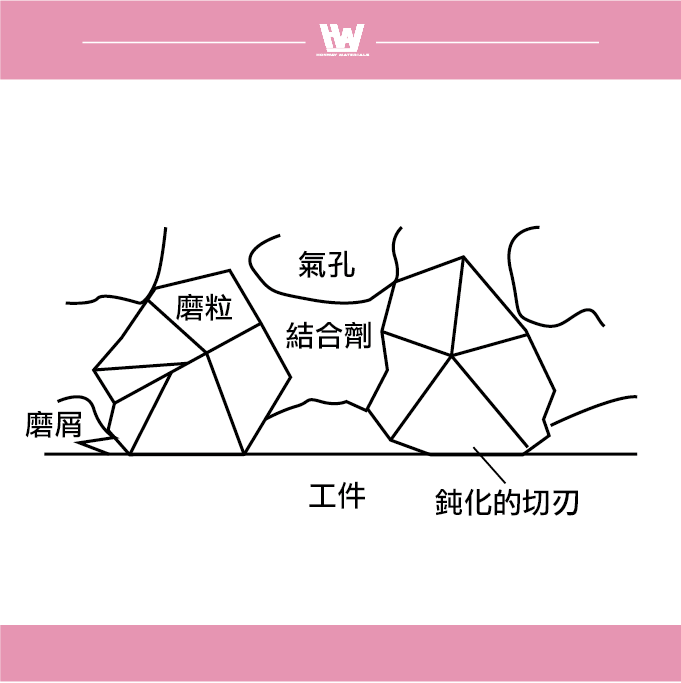
Four states that often occur in grinding wheels
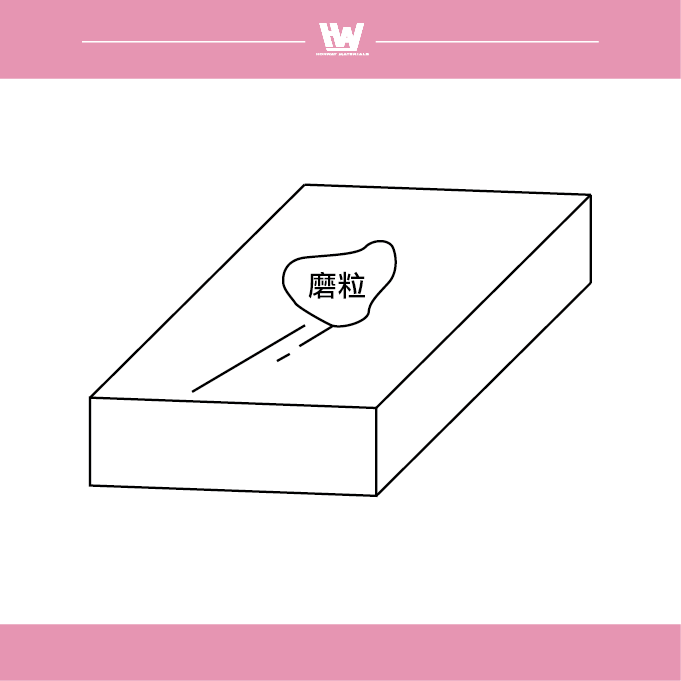
The grinding phenomenon even if the grinding conditions are constant, does not maintain a certain shape in time, the cutting edge on the grinding wheel changes according to the thermal and mechanical load acting on it, and the discharge state of the grinding chips changes accordingly, and the type of change can be divided into four types: 1. Shedding type, 2. Normal shape, 3. Packing type, 4. Smooth shape
Shedding type
In shedding grinding operations, when the cutting edge of the abrasive is worn out, the grinding resistance increases, resulting in a large amount of abrasive detachment. In this case, the spacing between the abrasive particles increases, and the surface of the grinding wheel appears rough.
- Abrasive chip shape: In the shedding type, the shape of the abrasive chips may appear to be fluid or sheared, which may affect the machining result.
- Grinding resistance increases: As the abrasive wears, the cutting efficiency decreases, resulting in an increase in grinding resistance.
- A lot of abrasive comes off: The abrasive falls off due to wear during the cutting process, which affects the overall machining performance.
- The lattice between abrasive particles increases: The gap between the abrasives becomes larger, making the surface of the grinding wheel rough.
- The grinding wheel surface is rough: The abrasive wear causes the surface of the grinding wheel to be uneven, which increases the difficulty of machining.
- Poor machining accuracy: It is not possible to achieve the desired machining accuracy by relying only on a specific amount of pink.
- The roughness of the machined surface is large: Due to the abrasive wear and the roughness of the grinding wheel surface, the final machined surface will be rough.
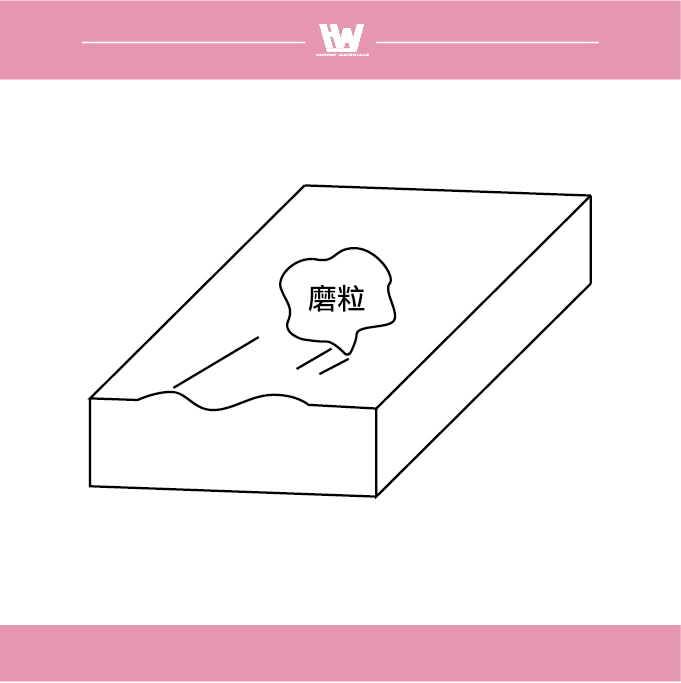
2. Normal type
When grinding, when the cutting edge of the abrasive is blunted, the grinding resistance increases. At this point, the abrasive splits open and a new cutting edge is revealed, which restores the original cutting force and maintains the desired grinding result.
- Grinding resistance: Although the grinding resistance is greater than that of the shedding type, it is still lower than that of other grinding methods.
- Small particle spacing: Abrasive particles are tightly packed to help improve cutting efficiency.
- Abrasive chip shape: Abrasive chips are non-sticky and are usually flow or shear.
- Grinding wheel wear: The wear and tear of the grinding wheel is less than that of the shedding type, which prolongs the service life.
- Smooth processing surface: provide good surface quality.
- High machining accuracy: It can achieve high machining accuracy.
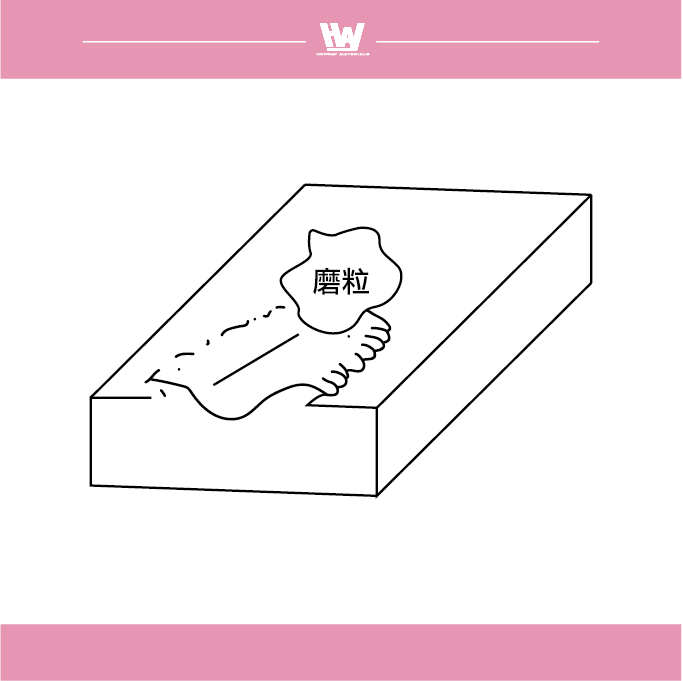
3. Stuffed type
In packing grinding, grinding chips adhere to the surface of the grinding wheel, which can hinder other grinding operations. The shape of the grinding chips is usually tear or melt, and these chips can form the cutting edge, further affecting the cutting results.
- Abrasive debris adhesion: Abrasive debris adheres to the surface of the grinding wheel, affecting the grinding efficiency.
- Grinding chip shape: common tear shape and melt shape, reducing cutting performance.
- High grinding resistance: It increases the resistance during grinding, which is easy to cause vibration.
- Machined surface quality: Tearing or chattering may occur on the machined surface, affecting the smoothness of the surface.
- Grinding wheel wear: The wear of the grinding wheel is greater than that of the normal type, which reduces its service life.
Trivia – chatter: refers to the phenomenon of small ripples or unevenness on the surface of the workpiece during processing or grinding. This phenomenon often affects the surface quality of the final product and can lead to substandard products.
4. Smooth
In smooth grinding, the abrasive is passivated to a state where it loses its grinding ability, resulting in a smooth surface of the abrasive and the entire grinding wheel being coated, which negatively affects the grinding effect.
- Abrasive chip shape: The abrasive debris is mostly tear or molten shape, which further affects the processing quality.
- Abrasive passivation: The abrasive loses its cutting ability and behaves as a fillet.
- Full Coverage: The entire grinding wheel surface is covered with smooth abrasives.
- Poor cutting force: The cutting force decreases significantly due to the passivation of the abrasive.
- High grinding resistance: The resistance during grinding increases, affecting efficiency.
- More heat: As the grinding resistance increases, so does the heat generated.
- Flutter marks and scorching: Chatter marks or surface scorching are common during processing.
Causes of the shape of the grinding wheel
In the case of grinding wheels, the grinding form varies depending on the particle size, structure, adhesion, type of abrasive, etc.
1. Condition for the occurrence of tamponade:
- The finer the granularity.
- The harder the bond.
- The denser the organization.
- Silicon carbide-based abrasives (large splitting).
- The amount of plunge, the amount of feed, and the speed of the workpiece increase.
- Grinding wheel speed is reduced.
2. Smoothing conditions:
- The finer the granularity.
- The harder the bond.
- The denser the organization.
- Silicon carbide-based abrasives (large splitting).
3. Falling off conditions:
- The amount of plunge, the amount of feed, and the speed of the workpiece increase.
- Grinding wheel speed is reduced.
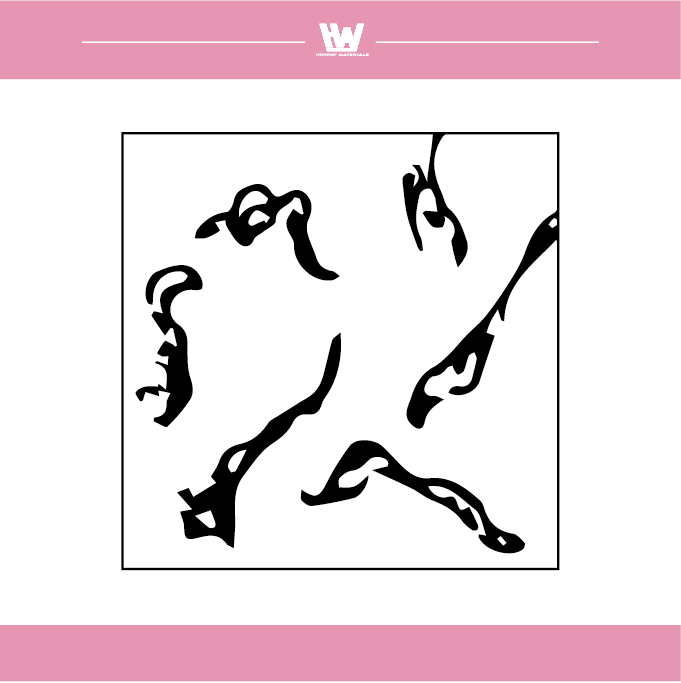
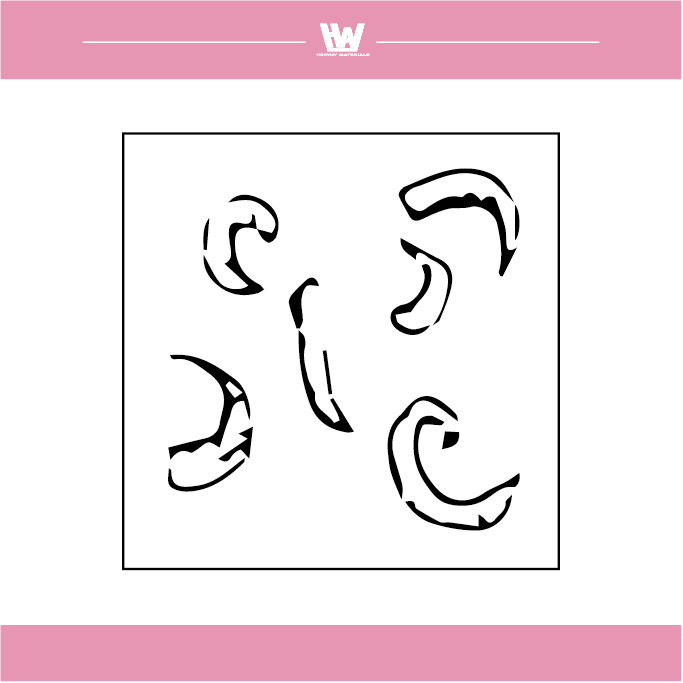
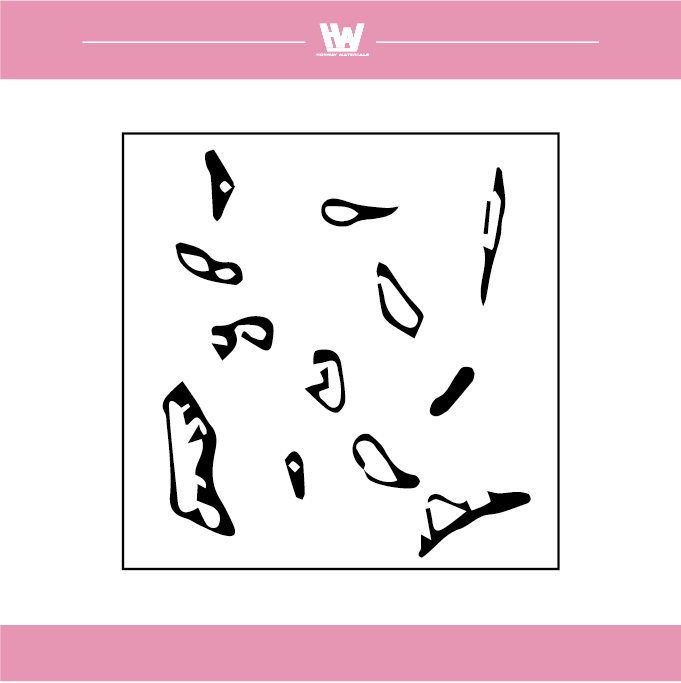
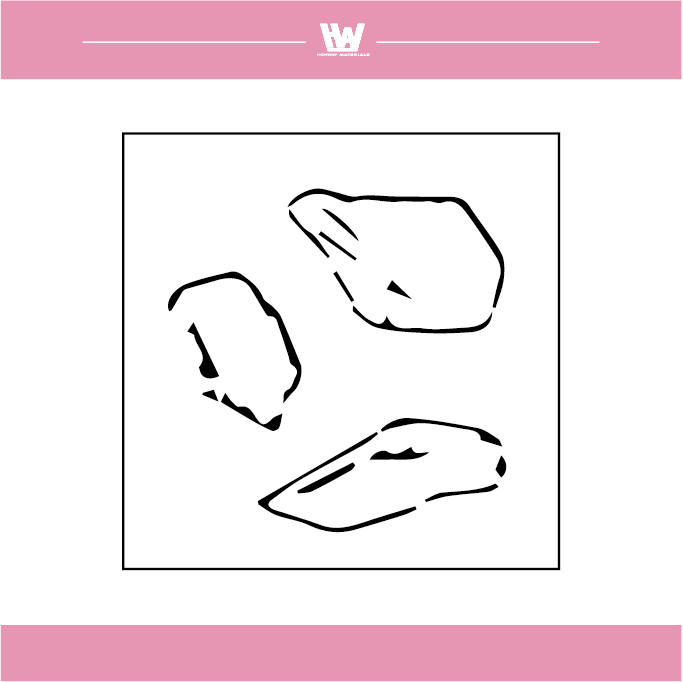
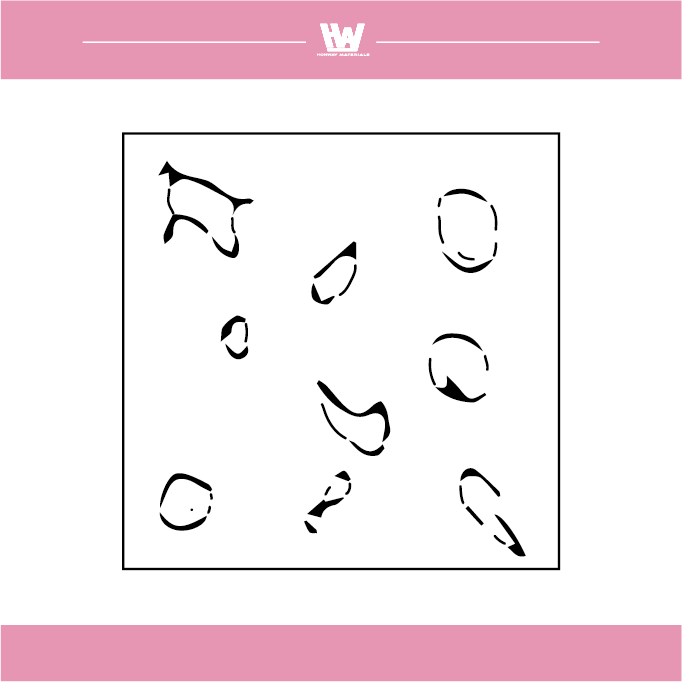
The shape of the scrap produced by grinding
1. Flow shape: The grinding chips are in the form of a bond, which mainly occurs when the cutting force of the grinding wheel is good.
2. Shear shape: Grinding chips are produced by good cutting forces, usually when grinding brittle materials.
3. Tear shape: The grinding chips are in the form of powder, which occurs when the cutting force of the grinding wheel is insufficient.
4. Forming a blade tip shape: Abrasive chips accumulate on the surface of the grinding wheel due to adhesion to form a structure similar to the tip of the cutting edge, which is common in the case of a plugged grinding wheel.
5. Melt shape: Powdery abrasive debris is overheated and scatters and melts into a ball or hemispherical shape, which mostly occurs when grinding and cutting off or using a tampon-shaped or smooth grinding wheel.
Conclusion
The structure of the grinding wheel, the characteristics of the abrasive grains, the grinding type and the shape of the grinding chips generated, the various conditions in the grinding process, such as particle size, adhesion, microdensity, abrasive type and grinding parameters, have a key impact on the machining results.
Proper parameterization ensures that the grinding wheel remains in ideal condition for efficient cutting and good surface quality; On the other hand, if the parameters are not correct, it may lead to undesirable conditions such as filling or smooth shape, which will affect the processing efficiency and product quality.
In order to achieve the best machining results, it is necessary to flexibly adjust the relevant parameters according to the characteristics of different materials and processing needs, and at the same time closely observe the morphological changes of the grinding wheel and grinding chips, and carry out necessary trimming or replacement to maintain a stable and efficient grinding process.
Action
- How to choose grinding wheel>>>How to Choose Between Diamond Wheels and CBN Wheels?
- The basic knowledge of abrasives that must be known>>>Grinding-Abrasive Introduction
- The Key Role of Grinding Wheel Performance>>Bond
- Whether the current measured surface roughness meets your expected goals>>>Comparison Chart of Grinding Polishing and Surface Roughness
- Is the current grinding wheel wear normally>>>What is the current status of the grinding wheel? – Electroplated Grinding Wheel Section
- Action>>>Diamond and CBN grinding wheel, Polishing abrasive, Polishing Equipment, Polishing Tools
- Review
We offer customized adjustments to the grinding process, tailored to meet processing requirements for maximum efficiency.
After reading the content, if you still don’t know how to select the most suitable option,
Feel free to contact us and we will have specialist available to answer your questions.
If you need customized quotations, you’re also welcome to contact us.
Customer Service Hours: Monday to Friday 09:00~18:00 (GMT+8)
Phone: +8867 223 1058
If you have a subject that you want to know or a phone call that is not clear, you are welcome to send a private message to Facebook~~
Honway Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/honwaygroup