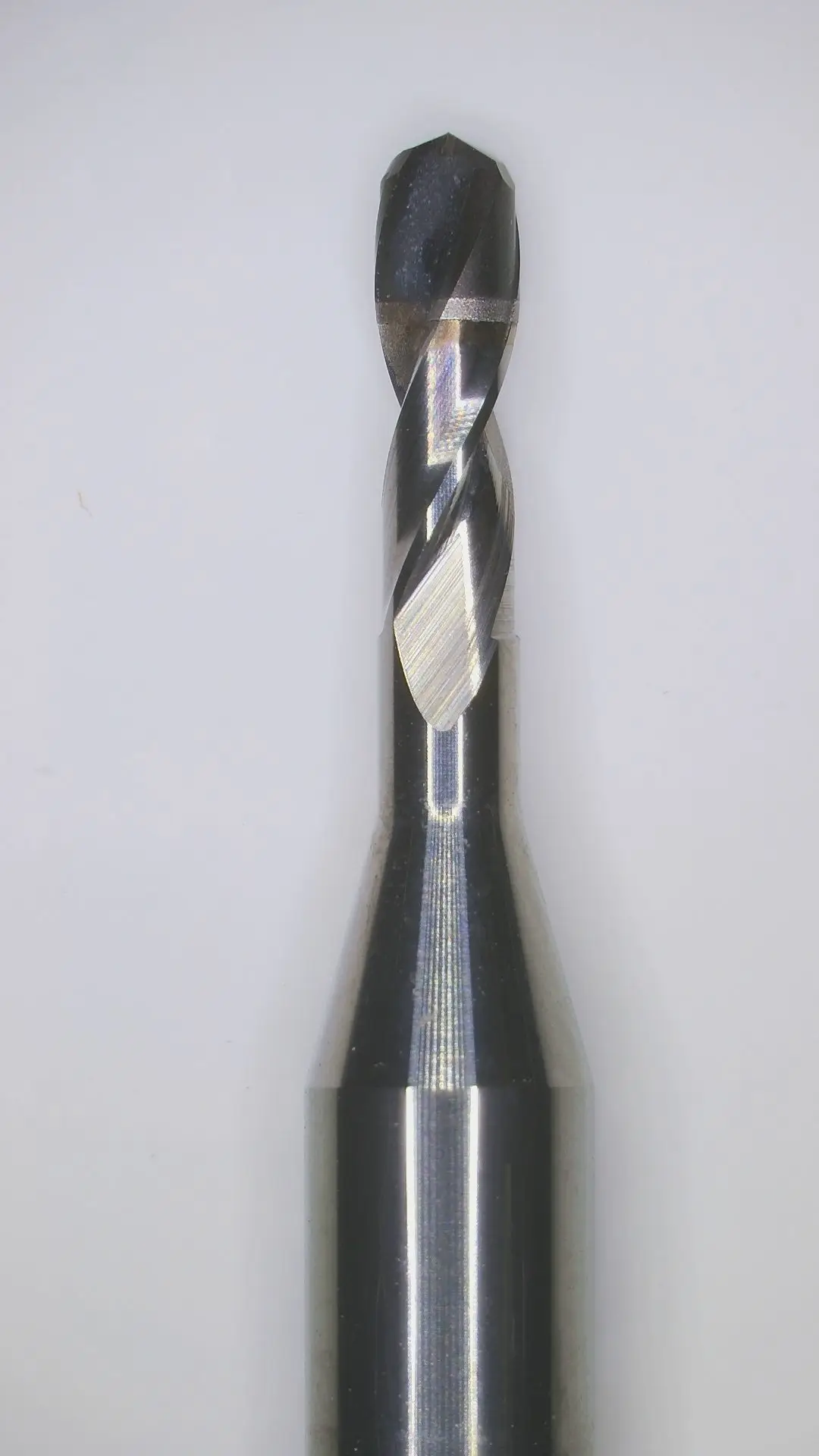
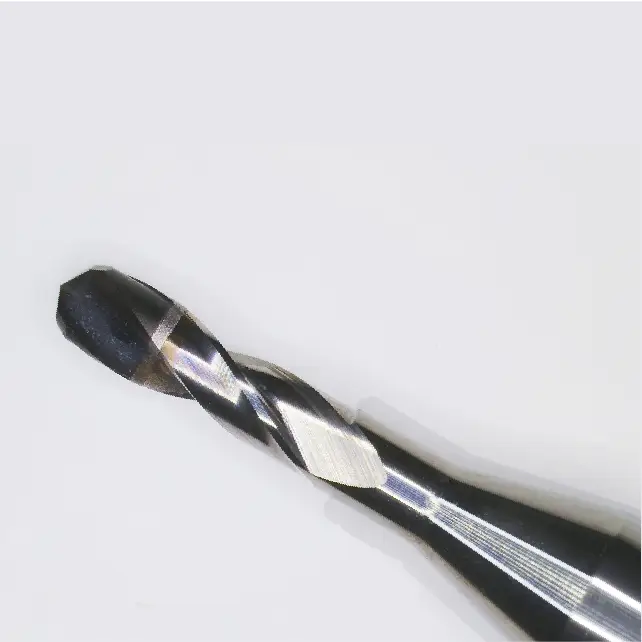
HCD.PM Cylindrical PCD Cutter – Product Features
Adjustable diamond particle size and cobalt content to match various wear resistance, impact resistance, and thermal conductivity. Cylindrical PCD cutters are ideal for micro-blade cutting with flexible designs to meet special requests.
- High hardness and wear resistance.
- Enables the design of complex blade shapes, suitable for processing materials such as aluminum alloys and ceramics.
- Cylindrical diamond tool blanks have no restrictions on the geometry of the drill bit design.
- The drill’s inclination angle can be designed and processed according to different machining requirements.
- The lifespan of PCD drills is 10 times longer than that of alloy tools.
Application areas:
- Suitable for various precision milling, drilling operations, CoWoS processes, and industries such as electronics, aerospace, medical devices, and semiconductors.
- Suitable for cutting various semiconductor substrates, including silicon carbide substrates, glass substrates, ceramic substrates, and alumina substrates.
Product features
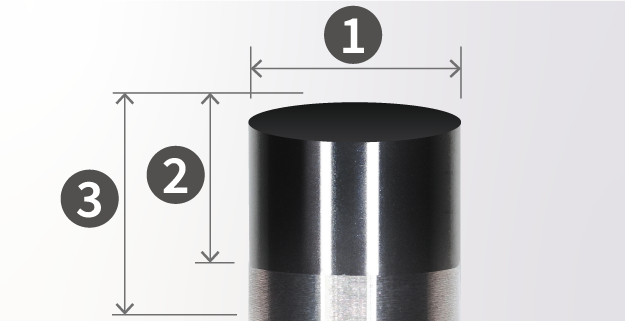
| Model | Product Types | Application | Granularity | 1. Diameter | Helix Angle | 2. Blade Length | 3. Matrix |
| HCD.PM | Cylindrical Type | Milling
Drilling |
Thin
Medium Thick |
Original blank size: ∅1.5~∅25
Finished blank size:∅3~∅25 |
N/A | 0.5~6 | 1~16 |
※ Unit of size(MM)
Material characteristics
Please note
1. Inclination Angle: Single-point PCD tools should not be aligned perpendicular to the grinding wheel center; they typically need to be inclined 10-15°.
2. Careful Placement: When placing the PCD tool into the collet, be sure to avoid collisions between the tool and the grinding wheel surface to prevent damage to the tool or the grinding wheel.
3. Avoid Overheating Damage: Do not quench hot dressing tools. When performing dry dressing, allow sufficient time for the PCD tool to cool down fully to avoid damage caused by overheating.
4. Select Appropriate Tools: When ordering PCD tools, consider the tool’s applicable range. Especially when machining ferrous metals, the chemical reaction between diamond and carbon in steel may accelerate tool wear.
5. Maintenance and Cleaning: When replacing tools, remove all broken tool fragments first to prevent secondary damage to the tools. Ensure that the processing equipment is stable, as unstable equipment is prone to vibrations, which can cause the tools to break.
6. Storage: When storing PDC tools, place them separately and do not place the tips facing each other to avoid damage to the tools.