Introduction to Chemical Element-Copper
Copper, with the chemical symbol Cu, is a soft metal that appears reddish-orange with a metallic luster when freshly cut. It has excellent ductility, along with high electrical and thermal conductivity, which makes it widely used in cables, electronics, and electrical components. Copper can form various alloys with other metals, such as sterling silver for jewelry, cupronickel for marine hardware and coins, and constantan for strain gauges and thermocouples. Bronze and brass are the most representative copper alloys, known for their superior mechanical properties and low electrical resistivity. Additionally, copper is a durable metal that can be recycled multiple times without losing its properties.
Table of Contents
Common Questions about Polishing Copper
1. Common Types of Copper
Brass: An alloy composed of copper and zinc that has excellent mechanical properties and wear resistance. It is often used to make precision instruments, ship parts, gun shells, and coins (such as five-yen coins).
Bronze: An alloy made of pure copper (red or copper) mixed with tin or other metals (such as lead or aluminum). Freshly made bronze has a golden brown appearance. Aluminum bronze has high strength, excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance, and is often used to manufacture high-load components such as bushings, gears, and marine propellers.
White copper: also known as copper-nickel alloy, it has hard strength, good plasticity and excellent corrosion resistance, and has high resistivity and is not easy to rust. These properties make it widely used in the manufacture of decorations, water supply equipment, instruments and currency.
2. What Kind of Surface Does Copper Produce After Polishing?
Polishing copper can create a smooth, reflective, mirror-like finish on the metal surface.
3. Does Copper Oxidize Easily?
Brass is resistant to corrosion, but when exposed to air, it can oxidize, causing black spots and an odor on its surface. While this patina is often considered part of brass’s appeal, the black spots become more noticeable as oxidation progresses. Additionally, exposure to water or sweat may cause a greenish “verdigris” similar to rust on iron.
4. Common imperfections
Orange peel effect: When coarse-grained aluminum alloy or copper alloy sheet blanks are drawn, bent or stretched, a rough morphology similar to orange peel may appear on the surface of the product. This phenomenon reflects uneven deformation between grains.
Spot oxidation: Copper reacts slowly with oxygen in the air or the mold is not cleaned in time or the environmental humidity is too high. Oxidation spots are easily formed on the surface, affecting the appearance and performance of the mold.
Scratches – The ground copper material is easy to stick to the surface of the abrasive, causing scratches as the grinding tool rotates, and it is difficult to improve the gloss.
5. Difficulties in polishing copper compared with other metals
Low hardness: Copper has lower hardness than other metals. If the rotation speed is too high during polishing, it will easily cause scratches and pits. It is more difficult to polish than other metals with high hardness.
Easy to block abrasives: Copper has good ductility, so the ground copper easily sticks to the abrasive grains, causing the abrasive grains to reduce the grinding force and affect the heat dissipation function.
Issues Affecting Subsequent Surface Polishing of Copper
Selection of mold material: The surface material of the mold in contact with copper may affect the oxidation rate of copper, because the surface characteristics of different materials will affect the adhesion of moisture and oxygen, thereby accelerating the oxidation reaction.
Heat treatment process: The process of heating and cooling a metal or alloy to change its physical and chemical properties. These processes are designed to improve properties such as strength, hardness, toughness and wear resistance of materials.
Roughness of the mold surface: Roughness has an important impact on the functionality of the mold because a smoother surface reduces friction, improves the surface finish of the molded product, and makes demoulding easier.
The shape of the mold surface: affects the ease and uniformity of polishing. Complex curved surfaces, edges and corners may lead to uneven polishing and reduced final surface quality.
Polishing process: It will significantly affect the polishing effect, including smoothness, efficiency and surface quality. Different polishing techniques (such as cloth wheel polishing, sandpaper polishing or abrasive polishing) have different characteristics in terms of processing speed, applicable materials and final surface state.
Selection of polishing tools: Different polishing tools (such as cloth wheels, abrasive discs or sandpaper) have different characteristics in terms of material, hardness and shape. Improper selection may cause surface scratches, uneven wear or failure to achieve the required gloss.
The initial surface quality of the workpiece directly impacts the time and difficulty of subsequent polishing. Understanding the various factors in the processing stages and choosing the appropriate processing methods can significantly enhance production efficiency, achieving greater results with less effort.
If there is a lack of effective copper polishing solutions, the following experimental results can serve as a reference, offering ideal solutions to address the various challenges encountered during the polishing process.
Copper Polishing Experiment
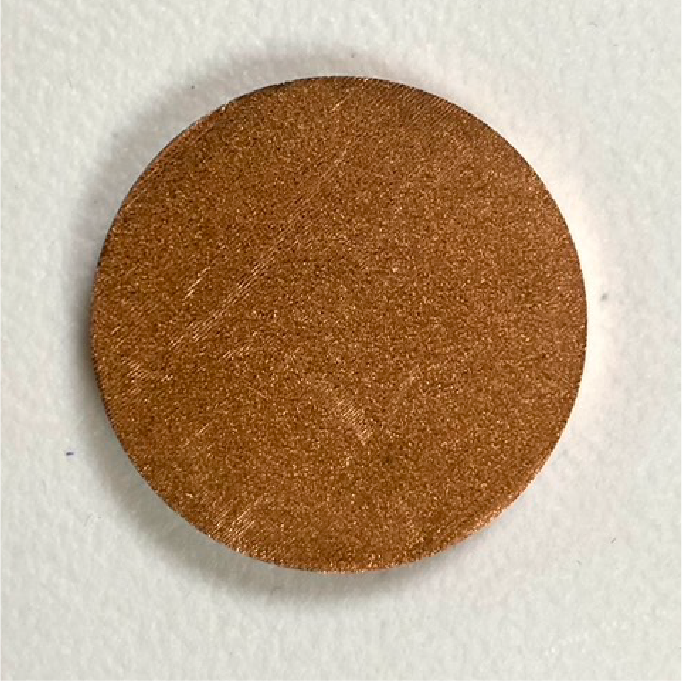
※Take red copper as an example
Copper is a metal with excellent electrical conductivity and ductility. Its applications are common in daily life and electronic parts.
However, during the polishing process, challenges are often encountered, such as surface spot oxidation, scratches, and lower hardness of the material, which can affect the final surface finish and overall performance.
In order to effectively solve these problems, Hongwei Laboratory conducted mechanical polishing experiments on copper to explore the impact of different polishing technologies and conditions on the polishing effect.
In the experiment, we evaluated the selection of polishing tools and polishing agents, aiming to optimize the polishing process and improve the surface finish and durability of copper, thereby improving its performance in practical applications.

Tools Preparation
1. Metallographic Grinding and Polishing Machine
2. Polishing pads: such as electroplating pads, resin pads, cerium oxide leather polishing pads and other models with different abrasive materials
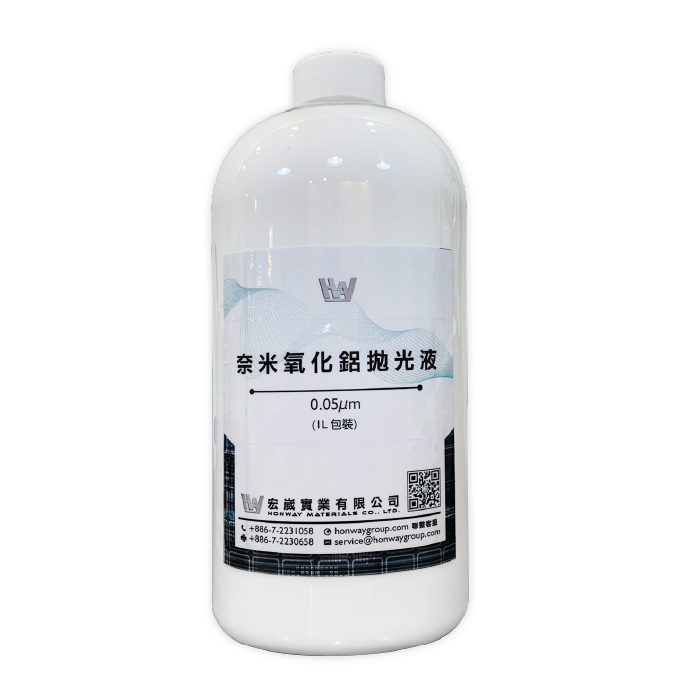
3. Polishing fluid: such as: nano diamond polishing fluid, alumina (cerium) polishing fluid, silicon dioxide, etc., used together
Polishing Processes of Copper

Electroplating disc-resin disc-cerium oxide leather polishing pad-diamond liquid-cerium oxide-alumina-silica
※Start from rough polishing and gradually transition to fine polishing to avoid excessively deep scratches caused by single polishing
Polishing Issues in Experiment
When copper comes into contact with liquids and is not cleaned promptly, white spots can easily form on the surface.
When using cerium oxide pads for polishing copper, if the polishing pad is too soft, it can easily scratch the surface.
Polishing pads that are too soft make it difficult to apply sufficient pressure during the polishing process, making it ineffective at removing surface defects and fine scratches.
Recommended Polishing Tools
Nano diamond polishing solution / Grinding solution / Suspension >>>Polishiing solution
- Best suited for: mechanical operation
- State: liquid (oil-based/water-based/alcohol-based)
- Polishing can be performed using a double-sided grinding machine, chemical mechanical polishing (CMP), or metallographic grinding.
- ※ Since the abrasive is in a free state, it is suitable for large-scale polishing.
- ※ If the surface of the workpiece is still rough, choose a polishing liquid with larger particles.
Alumina / Cerium oxide polishing solution / Grinding solution / Suspension >>> Polishing solution
- Best suited for: mechanical operation
- Status: Liquid
- Scope of application: Generally used after diamond compound
- ※ Possesses the ability of repairing polishing marks on the workpiece.
- ※ Cerium oxide is recommended to be used with tools at low speed.
Polishing pad / Grinding pad >>>> Metallographic consumables
- Materials:
- Contains abrasive: Cerium oxide leather, electroplating, resin
- Without abrasives: silk, leather, polyurethane (black velvet), woven fabric, fleece, porous, hard cloth, soft cloth, etc.
Practical Applications of Copper
Copper Pipe and Fittings: Copper pipe and fittings are used in construction, refrigeration and HVAC systems because of their good thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
Electronic products: It is widely used in electronic products, such as in printed circuit boards, cables, transformers and generators.
Marine and Automotive: Used in the manufacture of propellers, coolers, engine parts, etc. for boats and automobiles.
Industrial machinery: It is also widely used in industrial machinery, such as brakes, transmission shafts, gears, etc.
Conclusion
Copper products are widely used in everyday life, spanning various fields from electronics and plumbing to decorative items. Therefore, understanding how to maintain the luster of metal surfaces is essential knowledge. For restoration professionals, a deep understanding of copper’s properties, copper alloys, and their practical applications can help in selecting the most suitable polishing tools and processing methods. This not only enhances the quality of the restoration but also reduces production costs and shortens processing time, making the entire restoration process more efficient and reliable, ultimately improving the overall quality and lifespan of the products.
Action
- Does the current measurement of surface roughness meet your expected target? >>> Comparison Table of Grinding and Polishing with Surface Roughness
- Common problems and solutions about metals>>> Metal Polishing Defect Repair Guide: Common Problem Solutions and Recommended Quality Materials and Tools
- How to solve >>> Six mold polishing techniques: How many do you know?
- Implement >>> polishing abrasives, polishing equipment, polishing tools
- Review
We offer customized adjustments to the grinding process, tailored to meet processing requirements for maximum efficiency.
After reading the content, if you still don’t know how to select the most suitable option,
Feel free to contact us and we will have specialist available to answer your questions.
If you need customized quotations, you’re also welcome to contact us.
Customer Service Hours: Monday to Friday 09:00~18:00 (GMT+8)
Phone: +8867 223 1058
If you have a subject that you want to know or a phone call that is not clear, you are welcome to send a private message to Facebook~~
Honway Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/honwaygroup