Grinding processing is a precision surface treatment technology, controlling the roughness of the processed surface is one of the keys to ensuring the quality of the workpiece in this process.
Surface roughness not only affects the appearance and texture of the product but also directly relates to its functionality, such as wear resistance and fatigue life. However, the grinding process can be influenced by various factors, including the choice of grinding wheel, depth of cut, and feed rate. If these factors are not precisely controlled, it may lead to undesirable surface roughness.
The article discusses the definition of surface roughness, influencing factors, and improvement methods, help readers understand how to effectively improve surface quality in grinding processing.
The primary goal of grinding is to achieve the desired processed surface. However, there are three major challenges in grinding processing:
- Smoothness of the machined surface: the control of surface roughness, the smoothness of the machined surface appearance, and how to meet the requirements.
- Accuracy of the machined surface: whether the machined surface meets the expected machined surface, involving the process of shape and size generation.
- Stability of the Surface Layer: This relates to whether the surface layer undergoes deterioration due to mechanical effects or thermal loads during the grinding process.
※This chapter mainly discusses the smoothness of machined surfaces
Table of Contents
Before getting into the topic, let’s make some additions.
Definition of Surface Roughness
Abbreviated as roughness.
Refers to the unevenness of the surface caused by processing or other processing processes at small intervals, these uneven features can affect the feel of the surface, imagine the feeling of touching a piece of paper and touching a piece of sandpaper, the surface of the sandpaper is rougher. According to JIS B 0601, surface roughness is mainly caused by factors such as the tool geometry during machining, the angle of the cutting tool, and the abrasive particles. For example, processes such as turning, milling, or grinding create specific bump features on the surface of the workpiece.
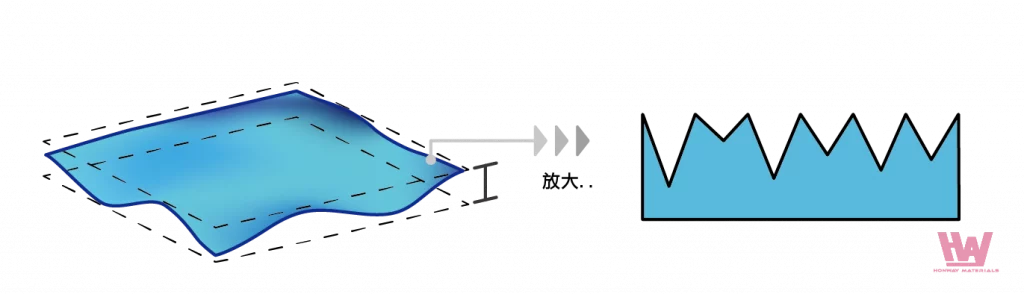
(Read more: What is surface roughness?)
Expression Method of Surface Roughness
There are many ways to represent surface roughness, but here are some common ones:
- Maximum height roughness Rmax (μm): Refers to the maximum vertical distance from the highest point to the lowest point within the surface roughness curve. It reflects extreme changes in the unevenness of the surface.
- Centerline Mean Roughness Ra (μm): Also known as arithmetic mean roughness, this is the average absolute deviation value taken from the sample section of the surface roughness curve. Ra is the most commonly used roughness parameter to reflect the degree of overall roughness.
- Ten-point average roughness Rz (μm): Calculated as the sum of the average heights of the five highest peaks and the average depths of the five lowest valleys in the roughness curve. Rz is primarily used to describe larger features of surface unevenness.
- Self-multiplying mean square root roughness Rrms (μm): Also known as rms roughness, it is obtained by taking the average of the squares of each point in the surface roughness curve that deviates from the center line, and then opening the square. RRMS has a higher sensitivity and can more accurately reflect surface properties.
(Read more: Terminology and definition of surface roughness)
The following table shows the representation of surface roughness, the differentiation, the relationship between the width of the datum and the triangulation symbol.
| Surface roughness indication | Surface Roughness Range (μm) | Triangulation signs | Width of the datum (length of one side (mm) |
| 0.1-S | 0.1 or less | ▽▽▽▽ | 0.3 |
| 0.2-S | 0.2 or less | ||
| 0.4-S | 0.4 or less | ||
| 0.8-S | 0.8 or less | ||
| 1.5-S | 1.5 or less | ▽▽▽ | 1 |
| 3-S | 3 or less | ||
| 6-S | 6 or less | ||
| 12-S | 12 or less | ▽▽ | 3 |
| 18-S | 18 or less | ||
| 25-S | 25 or less | ||
| 35-S | 35 or less | ▽ | 5 |
| 50-S | 50 or less | ||
| 70-S | 70 or less | ||
| 100-S | 100 or less | ||
| 140-S | 140 or less | 10 | |
| 200-S | 200 or less | ||
| 280-S | 280 or less | ||
| 400-S | 400 or less | ||
| 500-S | 500 or less |
(Read more: Comparison Chart of Grinding Polishing and Surface Roughness)
These parameters are selected according to the actual needs and are used to describe the different emphases of the surface roughness. Ra is the most commonly used standard in industry, while Rz and Rmax are often used to inspect roughness features for special functions or applications.
※Rz is often used in Japan.
Start the topic:
Effect of grinding conditions on surface roughness of machined surface
Before machining, we first think about how to achieve the ideal quality of the “surface”, and then think about the grinding process, the corresponding abrasives and the selection of tools to achieve it.
After summarizing the following general theories:
- The higher the workpiece speed, the larger the surface roughness.
- The smaller the circumferential speed of the grinding wheel, the larger the surface roughness.
- The smaller the radius of the grinding wheel and the workpiece, the larger the surface roughness.
- The amount of plunge is not directly related to the face roughness.
- The larger the particle size of the abrasive, the larger the surface roughness.
- The larger the equivalent tip angle of the abrasive, the smaller the surface roughness.
In order to obtain a good machining surface, it is necessary to homogenize the cutting edge height of the surface of the grinding wheel and increase the density through appropriate trimming.
In addition, we will discuss and propose simple solutions in two parts to provide first-line judgment on the spot
- The effect of the particle size of the abrasive and the binder on the surface roughness
- Grinding operation process and environmental factors: the amount of penetration, feed, vibration influence, residual grinding and other influences
The effect of the particle size of the abrasive and the binder on the surface roughness
Effect of granularity:
The particle size, that is, the number of the abrasive, when the number of the grain number is smaller, that is, the coarser the particle, for example, the grain number of #36 is much coarser than that of #600, and the same way #600 is coarser than #3000.
(If it sounds vague, the quickest way is to go to a nearby hypermarket or art club to actually feel the touch of sandpaper)
Here are a few conclusions:
- The finer the particle size (number), the lower the coarseness (smoother) of the processing surface.
- Under the same grinding method, the improvement effect of particle size reduction is more significant.
- The uniformity and consistency of abrasives and toughness help to improve the quality of the machined surface.
- Appropriate grinding wheel structure (structure, adhesion) and working conditions can achieve the effect of fine-grained abrasives.
Effect of degree of adhesion:
The degree of adhesion refers to the strength of the abrasive adhesion to the grinding wheel (we use soft and hard to refer to it).
This was referring to the strength of the adhesion of the “binder” (electroforming, metal, ceramic, resin) rather than the strength of the abrasive itself.
After selecting the appropriate strength and processing method, one of the important points is that “hard bonded grinding wheels help to improve the machining surface”.
But! Wheels being too hard can also lead to the following problems:
- Smooth, grinding wheel causage
- Grinding Burn
- The thickness of the surface metamorphic layer increases
- Reduced abrasion resistance
The reason is that the strong adhesion of the grinding wheel has a good effect of sticking to the abrasive, which can provide a good “surface” effect, but it will make the abrasive less likely to fall off, resulting in the above problems, which need to be noted.
Grinding operation process and environmental factors: the amount of penetration, feed, vibration influence, residual grinding and other influences
Effect of cutting amount (depth of feed):
With the increase of the cutting amount, the surface roughness increases proportionally.
The cutting depth of the abrasive is proportional to the square root of the cutting amount, and the cutting force increases, resulting in the following situations:
- The cutting edge is damaged and deteriorated
- The roughness of the machined surface deteriorates due to the influence of secondality
- Mechanical vibration enhancement
Method: If you find that the quality of the surface is reduced or the mechanical vibration is too serious, it is recommended to re-examine and adjust the setting of the cutting amount and the near-feed amount, and if there is no problem, you can refer to other influence problems to deal with.
Effect of feed amount:
- The higher the feed rate, the surface roughness increases linearly.
Method: It can be adjusted together with the cutting amount, and if there is no problem, you can refer to other impact problems to deal with.
Effect of Vibration:
The relative vibration between the grinding wheel and the workpiece causes:
- The cutting edge density decreases, the surface thickness increases, and especially the surface undulation increases
- The grinding wheel surface is beaten by the workpiece, and the grinding wheel abrasive falls off, further increasing the surface thickness
Method: The cause of vibration is not only caused by feed and cut-in, but also sometimes because of the environment, the following we have compiled a few methods to provide evaluation:
Environmental factors:
1. Check the ground level: confirm whether the ground level screws of the equipment are flush and touch the ground, and strictly use the level to check the horizontal status of the equipment before and after the equipment. If it is not properly adjusted, it may cause resonance of the machine tool and cause vibration.
2. The floor is not solid: if the above steps are adjusted or is it vibrating? That could be the hollow inside the floor. You can go to the hardware store to buy a rubber mat with a thickness of 6-10mm and pad it at the foot of the equipment (it is recommended to loosen the floor screws), which can be a good shock absorption.
※Supplementary station: As far as the floor is not solid, it cannot be said that it is a problem of ground processing quality, but the influence of material selection, and the solid plate will be more solid than the cement grouting, and the hollow floor is easy to resonate.
3. Equipment resonance: still no results? Separate devices that are prone to large vibrations.
※Reason: If you are performing precision surface grinding, it is not suitable for use with machine tools that are prone to vibration, such as punches and lathes. How can you tell? Turn off the grinder and feel it with your hand on the grinder, if you feel vibration, it means that it is affected.
The equipment itself and processing:
1. Uneven grinding wheel particle size: The use of uneven grinding wheels with abrasives is easy to cause unstable center of gravity and vibration during rotation
2. The size of the flange hole is wrong: the flange hole with the wrong size is easy to jump up and down after installation, resulting in vibration, so be sure to confirm the correct size when purchasing.
※Supplementary station: This is important! Incorrect flange holes can make the grinding process prone to bursting and danger and require special attention. Generally speaking, the high-quality flange wheel does not need to be corrected, and the grinding wheel can be used directly after it is repaired, but if the flange wheel is crooked, 1. You can use the balance weight, 2. Change the flange.
3. Feed amount and cutting amount: Excessive cutting amount and feed speed can easily cause the grinding wheel to shake, and in serious cases, it may deform the grinding wheel spindle, and the gains outweigh the losses. It is recommended to reduce the amount of feed and plunge processing.
Effect of Residual Wear:
Initially, the tip of the grinding wheel does not fit perfectly to the machined surface, resulting in unremoved material residue on the surface of the workpiece. These gaps generate sparks when grinding, and as the surface becomes smoother, the amount of residual wear decreases, and the surface thickness decreases.
The method of improving the roughness can reduce the amount of residual grinding and improve the roughness by increasing the number of grinding, reducing the amount of cutting and feeding, such as: when grinding, the initial amount of cutting to the final amount of cutting gradually becomes 0, and if you grind for many times, you can get a 1μm machined surface using a #36 grinding wheel.
Summary-The reasons for the large surface roughness in the grinding process are as follows:
- The amount of residual wear is large
- Deformation of the grinding wheel spindle
- Vibration
- Grinding wheel wear
Conclusion
Surface roughness is an important indicator to measure the quality of grinding processing, which directly affects the surface texture and functionality of the workpiece. In the grinding process, many factors such as workpiece speed, grinding wheel circumferential speed, abrasive particle size, bonding, and plunge amount will affect the roughness of the machining surface. Precise control of these parameters helps to achieve the desired surface smoothness and reduces the negative effects of excessive roughness, such as abrasive shedding, scorched grinding and surface deterioration. The key to improving roughness is to optimize the grinding conditions, including selecting the right grinding wheel, controlling the feed rate and plunge amount, and performing reasonable dressing and multiple grinding. By doing so, we can not only improve the surface quality, but also extend the service life of the workpiece and achieve high-precision machining.
Action
- How to choose grinding wheel>>>How to Choose Between Diamond Wheels and CBN Wheels?
- The basic knowledge of abrasives that must be known>>>Grinding-Abrasive Introduction
- The Key Role of Grinding Wheel Performance>>Bond
- Various aspects of grinding wheel abrasive grains>>The Grinding Effect of the Grinding Wheel Particles
- Coarseness measurement – line vs. surface>>Differences Between RA and SA
- Differences in various measurements>>Terminology and definition of surface roughness
- The surface is not rough, the light is not smooth>>What is surface roughness?
- Whether the current measured surface roughness meets your expected goals>>>Comparison Chart of Grinding Polishing and Surface Roughness
- Is the current grinding wheel wear normally>>>What is the current status of the grinding wheel? – Electroplated Grinding Wheel Section
- Action>>>Diamond and CBN grinding wheel, Polishing abrasive, Polishing Equipment, Polishing Tools
- Review
In terms of grinding, we offer customized adjustments that can be modified according to processing needs to achieve maximum efficiency
After reading the content, if you still don’t know how to select the most suitable option,
Feel free to contact us and we will have specialist available to answer your questions.
If you need customized quotations, you’re also welcome to contact us.
Customer Service Hours: Monday to Friday 09:00~18:00 (GMT+8)
Phone: +8867 223 1058
If you have a subject that you want to know or a phone call that is not clear, you are welcome to send a private message to Facebook~~
Honway Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/honwaygroup
You may be interested in…
[wpb-random-posts]

