As modern industry demands increasingly efficient and precise machining of high-hardness materials, traditional abrasives struggle to meet these requirements. In this context, the emergence of super abrasives has marked a significant milestone in industrial technological advancement.
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN), a synthetic material second only to diamond in hardness, has rapidly become an essential abrasive for processing high-hardness materials due to its exceptional durability, high-temperature stability, and chemical inertness.
CBN’s superior properties have allowed it to address the challenges of high-performance machining, providing solutions where diamond abrasives fall short, particularly in scenarios involving ferrous materials or elevated temperatures. Its adoption has driven advancements in various high-tech sectors.
This article provides a detailed exploration of the properties, applications, and profound impact of CBN abrasives on industrial development, helping readers gain a deeper understanding of how to utilize this advanced material effectively.
Table of Contents
Development History of Super Abrasives
In pursuit of higher quality and efficiency in industrial processing, researchers developed super abrasives such as diamond abrasives and cubic boron nitride (CBN).
Early Applications of Natural Diamond (Pre-1950s)
Before the 1950s, the industrial use of abrasives was limited to natural diamonds. High-quality diamonds were crafted into single-point tools for precision operations, while lower-quality diamonds were crushed and used as abrasives for grinding or cutting tools.
Invention and Application of Synthetic Diamonds (Late 1950s)
The late 1950s witnessed a revolutionary breakthrough with the successful synthesis of man-made diamonds.
Synthetic diamonds, unlike natural ones, could be manufactured for specific applications, rapidly becoming a dominant abrasive material. They found wide-ranging uses, including grinding, cutting, honing, drilling, dressing, and turning.
Consumption of Synthetic Diamonds (Modern Era)
Today, over 100 million carats of synthetic diamond abrasives are consumed annually worldwide, about one-third is used in grinding applications, and approximately half of the abrasives in grinding are dedicated to machining hard materials like tungsten carbide.
Emergence of Cubic Boron Nitride (Late 1960s)
In the late 1960s, another significant technological leap occurred with the synthesis of cubic boron nitride (CBN), a super abrasive with hardness second only to diamonds. CBN’s unique properties and high value quickly made it a favorite for industrial applications.
Development of CBN Abrasives (From the 1980s)
By the early 1980s, annual global consumption of CBN abrasives had surpassed 10 million carats, cementing its critical role in industry. Meanwhile, CBN began to replace traditional abrasives like aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) and, together with synthetic diamonds, is expected to dominate the abrasive market.
The following will focus on the characteristics and applications of cubic boron nitride abrasives.
Introduction to Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN)
CBN has an atomic structure similar to diamond, granting it exceptional hardness—just slightly below that of diamond. However, unlike diamonds, CBN is entirely synthetic and does not occur naturally.
CBN is created by converting hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) into a cubic crystalline structure under extreme conditions, with high temperature (1500–2000°C) and high pressure (50,000–90,000 atmospheres), through the catalyst facilitates the transformation process, resulting in a high-performance super abrasive.
CBN was developed to overcome the limitations of diamond abrasives in specific applications, particularly in the machining of iron-based, nickel-based, and cobalt-based materials, these materials’ chemical properties make them incompatible with diamonds, thus CBN is an ideal choice for processing such high-hardness, specialized materials.
Supplementary Knowledge: A catalyst is a substance that accelerates a chemical reaction by providing an alternative pathway with lower activation energy. It remains chemically unchanged before and after the reaction. Catalysts are vital in processes like the synthesis of CBN.
Characteristics of Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN)
High hardness
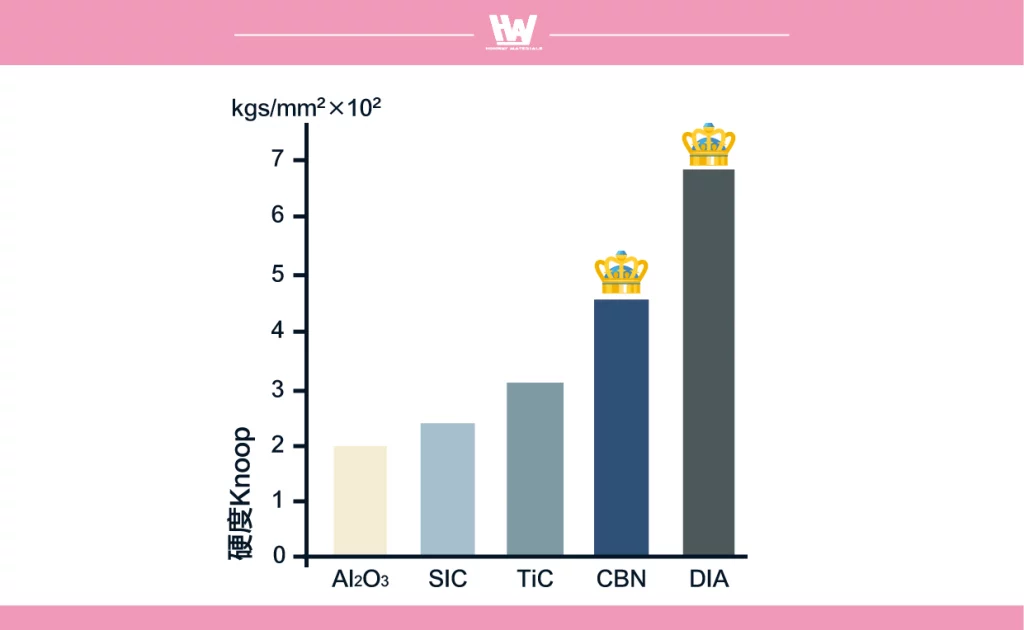
- CBN’s hardness is second only to diamond, surpassing silicon carbide and roughly twice that of aluminum oxide.
- CBN abrasives are renowned for their sharp, durable, and wear-resistant cutting edges, particularly in robust CBN applications.
Chemical Stability
- CBN exhibits excellent chemical stability at room temperature, making it resistant to reactions with workpiece materials.
- Compared to diamond, CBN offers superior chemical stability in high-temperature environments, effectively resisting oxidation and chemical corrosion.
High-Temperature Stability
- At approximately 900°C, CBN forms a protective boron nitride oxide film, preventing further oxidation.
- CBN maintains its thermal stability up to 1300°C, delivering exceptional performance in high-temperature processing without degradation from heat exposure.
Overcoming Diamond Abrasive Limitations
- CBN is particularly suitable for grinding and processing high-hardness metals such as iron-based, nickel-based, and cobalt-based alloys.
- It addresses diamond’s shortcomings in high-temperature and specific material processing, where diamonds are prone to oxidation or chemical reactions.
Superior Machining Capabilities
- CBN offers higher cutting efficiency than conventional abrasives, enabling rapid material removal and achieving high-precision results.
- During grinding, CBN particles naturally fracture to form new sharp cutting edges, extending tool life while maintaining machining performance.
High Wear Resistance
- CBN grinding wheels exhibit low wear rates, effectively extending their lifespan, reducing replacement frequency, and lowering costs.
Comparison of CBN and Diamond in Terms of Chemical Stability and High-Temperature Performance
The chemical stability of abrasives is an important factor in measuring their performance. While diamond possesses higher hardness (Knoop hardness ~7000) than CBN (Knoop hardness ~4700), CBN outperforms diamond in chemical and thermal stability during steel grinding.
Diamond’s High-Temperature Challenges:
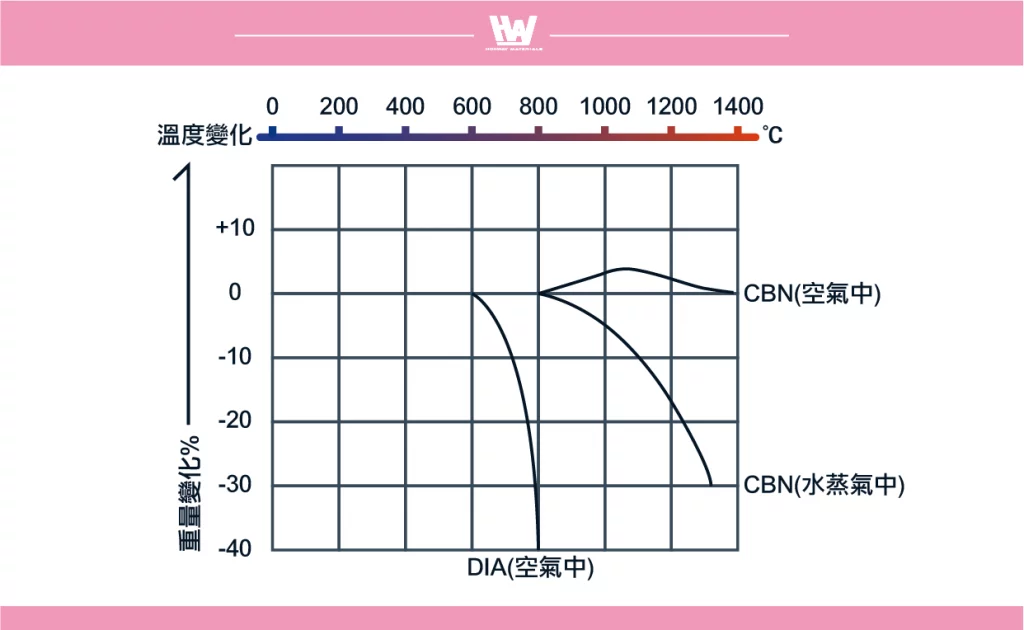
- At room temperature, the chemical properties of diamond and CBN are relatively stable, but in a high temperature environment, diamond is easily oxidized and graphitized.
- At 600–700°C, diamond begins to oxidize, ultimately converting to carbon dioxide and losing hardness, which compromises its abrasive capabilities.
- As a carbon-based material, diamond reacts with elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, chromium, and vanadium in workpieces, forming carbides and experiencing rapid wear.
CBN’s High-Temperature Performance:
- CBN starts to oxidize at ~900°C, but the resulting boron nitride oxide film protects the crystal from further oxidation.
- This protective layer remains effective up to 1300°C, ensuring that CBN retains its thermal stability and resists heat-induced degradation during grinding.
CBN has better chemical and thermal stability than diamond, and also unlike diamond, CBN is resistant to chemical attack from iron, cobalt, and nickel, making it the optimal abrasive choice for processing iron alloys, cobalt-based alloys, and nickel-based superalloys.
Applications of Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN)
CBN is a superabrasive specifically designed for processes such as grinding, honing, cutting, rubbing, and polishing. Its superior hardness and outstanding machining performance allow it to surpass traditional abrasives like white aluminum oxide in precision grinding and cutting applications.
CBN is highly effective for machining various high-hardness and wear-resistant materials, including:
- Tool and mold steel
- Carbon and alloy steels
- Iron casting
- Stainless steel
- Aerospace alloys
- Other wear-resistant alloys
Due to its efficiency and durability, CBN is particularly well-suited for high-volume production and intermediate tool use across several industries:
- Automotive Industry: Machining engine components, transmission systems, and vehicle parts.
- Hydraulic Components Industry: Processing high-precision parts to meet strict accuracy demands.
- Bearing Manufacturing: Ensures consistent and high-precision finishing.
- Aerospace Industry: Handles high-strength, wear-resistant aerospace materials with precision.
- Cutting Tool Manufacturing: Ideal for machining cutting tools and related high-hardness products.
While both diamond and CBN are superabrasives suitable for machining high-hardness and high-strength materials, CBN is the preferred choice for grinding materials containing iron-group elements.
Conclusion
CBN’s exceptional hardness, durability, high-temperature stability, and chemical stability make it an indispensable superabrasive in modern industrial applications. It overcomes the limitations of diamond abrasives in high-temperature and specific material processing, excelling in grinding, honing, cutting, rubbing, and polishing operations. Particularly effective for machining tool and die steels, carbon and alloy steels, stainless steel, aerospace alloys, and other wear-resistant materials.
Due to its unique characteristics, CBN plays a pivotal role in automotive manufacturing, hydraulic component precision engineering, bearing production, aerospace material machining, cutting tool manufacturing.
As a preferred solution for high-hardness material machining, CBN leads the advancement of modern industrial precision machining technology to new heights.
Action
- How to choose grinding wheel>>>How to Choose Between Diamond Wheels and CBN Wheels?
- The basic knowledge of abrasives that must be known>>>Grinding-Abrasive Introduction
- The Key Role of Grinding Wheel Performance>>Bond
- Whether the current measured surface roughness meets your expected goals>>>Comparison Chart of Grinding Polishing and Surface Roughness
- Various aspects of grinding wheel abrasive grains>>The Grinding Effect of the Grinding Wheel Particles
- What you need to know about super abrasive diamonds>>Introduction to Abrasives – Diamonds
- How to choose suitable traditional abrasives>>Selecting the Optimal Abrasive Based on Material Characteristics
- Different grinding states of cutting edge>>In-depth understanding of grinding wheel cutting edge shapes, variations, and self-sharpening mechanisms
- Action>>>Diamond and CBN grinding wheel, Polishing abrasive, Polishing Equipment, Polishing Tools
- Review
We offer customized adjustments to the grinding process, tailored to meet processing requirements for maximum efficiency.
After reading the content, if you still don’t know how to select the most suitable option,
Feel free to contact us and we will have specialist available to answer your questions.
If you need customized quotations, you’re also welcome to contact us.
Customer Service Hours: Monday to Friday 09:00~18:00 (GMT+8)
Phone: +8867 223 1058
If you have a subject that you want to know or a phone call that is not clear, you are welcome to send a private message to Facebook~~
Honway Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/honwaygroup
You may be interested in…
[wpb-random-posts]

