Table of Contents
What is ESG?
ESG is a corporate evaluation framework centered on sustainable development, encompassing the three dimensions of Environmental, Social, and Governance, aimed at assessing a company’s impact on and commitment to society and the environment. Companies should conduct business activities without causing negative impacts on the broader environment or society.
The concept was first introduced by the United Nations Global Compact in 2004 to encourage companies to improve their performance in environmental protection, social responsibility, and corporate governance. ESG also includes details on talent development and creating a positive workplace, emphasizing corporate responsibility toward employees, society, and the natural environment, and thus has become a crucial standard for measuring sustainable competitiveness.
What Are the ESG Indicators?
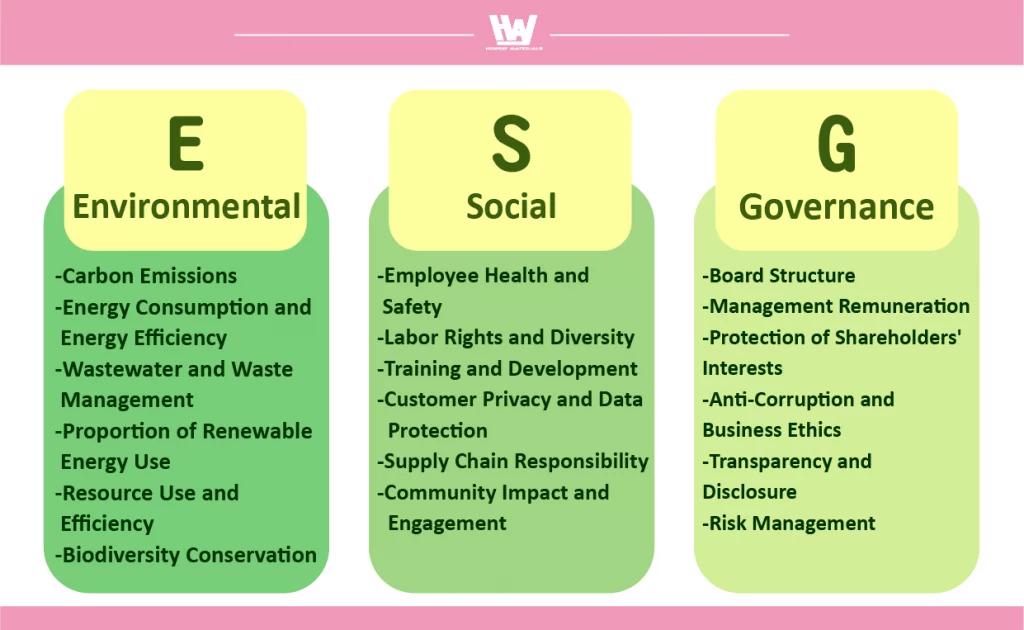
1. Environmental
“Environmental Sustainability” emphasizes that companies should pay attention to environmental issues in their operations, striving to reduce damage to ecology and the environment. Evaluation standards mainly focus on how companies address and manage challenges related to environmental protection, ecosystem balance, and climate change, taking specific measures in areas such as resource use, waste management, and carbon emission reduction to demonstrate their commitment to environmental sustainability.
Carbon Emissions: The amount of CO₂ and other greenhouse gases emitted by a company in production, transportation, and other operational activities.
Energy Consumption and Efficiency: The total energy consumption and energy efficiency of a company.
Wastewater and Waste Management: How a company manages and processes industrial wastewater, hazardous substances, and other waste materials.
Proportion of Renewable Energy Usage: The percentage of renewable energy, such as wind or solar power, in a company’s total energy consumption.
Resource Use and Efficiency: This includes the consumption and efficiency of resources such as water, wood, and metals, as well as whether sustainable procurement policies are in place.
Biodiversity Protection: Whether a company takes actions to protect and support ecosystems, avoiding damage to natural habitats.
2. Social
“Social Engagement” refers to a company’s commitment to improving its social impact, fulfilling its responsibilities toward society. Evaluation standards cover both internal and external stakeholders, including employees, customers, suppliers, and communities. Companies should strive to provide a positive work environment, support social welfare initiatives, uphold supply chain ethics, and contribute to overall social well-being.
Employee Health and Safety: Evaluates the safety of the work environment, availability of regular health and safety training, and the rate of workplace incidents.
Labor Rights and Diversity: Assesses whether the company promotes gender equality, racial diversity, and protection of labor rights.
Training and Development: Measures whether the company provides sufficient education and training resources to support employees’ career development.
Customer Privacy and Data Protection: Assesses measures to protect customer privacy and the transparency of data processing, which is particularly crucial in industries like finance and digital technology.
Supply Chain Responsibility: Evaluates if the company requires suppliers to meet environmental and social standards and monitors the ethical responsibilities of the supply chain.
Community Impact and Engagement: Measures the company’s contributions to local communities, such as charitable donations, volunteer work, and community investments.
3. Governance
“Corporate Governance” emphasizes the importance of a company’s commitment to effective management practices to safeguard its reputation and promote long-term growth. Evaluation standards encompass all facets of corporate operations, from high-level decision-making and board structure to internal controls and risk management. A robust governance system ensures that the company meets standards for compliance, transparency, and ethical conduct, building stakeholder trust and reinforcing a foundation for sustainable development.
Board Structure: Examines board diversity, independence of board members, and their professional backgrounds.
Executive Compensation: Assesses if management’s compensation is reasonable and aligned with company performance and ESG goals.
Shareholder Rights Protection: Evaluates if transparent voting systems are in place to protect the interests of minority shareholders.
Anti-Corruption and Business Ethics: Reviews the company’s anti-corruption measures and adherence to anti-money laundering and ethical business standards.
Transparency and Disclosure: Determines whether the company openly discloses operational status, financial statements, and ESG performance.
Risk Management: Assesses the company’s risk management framework, including how it addresses market risks, environmental risks, and policy changes.
What’s the Differences Between CSR, SDGs and ESG?
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) offers a broad direction for companies aiming for sustainable development, while ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) and SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals) provide specific frameworks for achieving sustainability.
CSR serves as a “general direction” for companies in sustainable development, outlining core responsibilities that should be prioritized. ESG provides a set of specific criteria to help companies implement CSR in three key areas: environmental responsibility, social commitment, and corporate governance. Meanwhile, SDGs give a detailed list of actionable goals that serve as “guidelines” for companies to address various social and environmental issues and contribute to global sustainability.
Main differences among the three:
ESG: Can be seen as an actionable version of CSR, offering specific standards for sustainable development.
CSR: Represents the globally shared goal of sustainable business operations and serves as a broad sustainability concept.
SDGs: United Nations’ 17 sustainable development goals, which align with ESG’s principles.
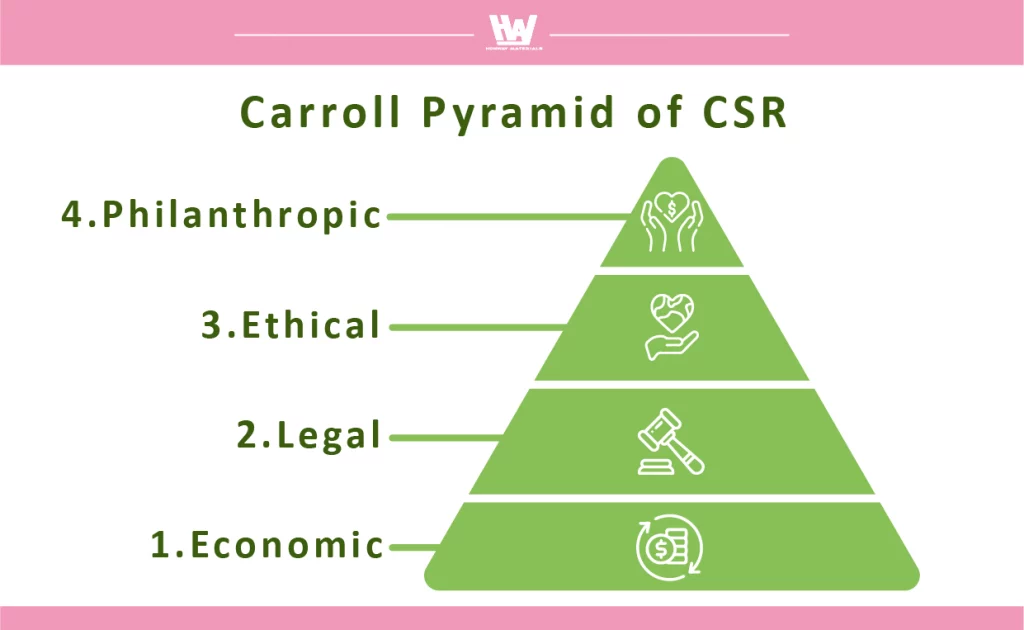
CSR is a globally promoted business philosophy that emphasizes balancing profitability and growth with social responsibility, community contribution, and environmental sustainability. The CSR pyramid includes four levels: “Economic Responsibility,” “Legal Responsibility,” “Ethical Responsibility,” and “Philanthropic Responsibility.”

SDGs are the United Nations’ 17 goals, addressing critical issues across economic, social, and environmental sectors. These goals, such as gender and racial equality, income inequality reduction, and climate change action, aim to inspire countries, companies, organizations, and individuals to incorporate these topics into their decisions and pursue a sustainable future.
The Importance of ESG
ESG serves as a standard for companies’ performance in environmental protection, social responsibility, and governance structure. It is crucial for reducing risks, enhancing brand image, attracting investment, improving employee satisfaction, and boosting long-term competitiveness. As stakeholders increasingly emphasize sustainable development, strong ESG performance not only meets regulatory requirements but also promotes innovation and operational efficiency, strengthens international competitiveness, and helps businesses achieve stable growth and sustainable development.
How Companies Can Implement ESG
Raise Overall Awareness: Through comprehensive education and training, help employees understand the importance of ESG and the company’s sustainable business objectives. Integrate these into the corporate culture to ensure all employees actively participate in and commit to ESG practices.
Increase Transparency: Proactively disclose company supply chains and ESG-related strategies. This reduces information asymmetry, enhances trust from investors and customers, and aids in self-assessment of sustainable practices. Additionally, companies should focus on ESG management within their supply chains to minimize external risks.
Systematize ESG Implementation: Companies should integrate ESG systematically across all departments, providing regular ESG training and guidance to ensure sustainable practices are deeply embedded in the organizational structure.
Enhance Risk Awareness: To tackle risks posed by environmental changes such as extreme weather, companies need to strengthen risk management awareness, conduct comprehensive risk assessments, and develop long-term strategies to address these challenges.
Promote Digital Management: Digital transformation supports ESG implementation. Using digital management tools, companies can reduce management costs, improve product quality, and enhance collaboration with supply chains, promoting efficiency and sustainable development.
Conduct Carbon Emissions Audits: To achieve net-zero carbon goals, companies can carry out carbon emissions audits and gradually increase the use of renewable energy. This reduces their carbon footprint, minimizes the environmental impact of production, and prevents market exclusion due to unachieved carbon reduction targets.
Challenges in Implementing ESG
Funding Constraints: Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often lack the resources that large corporations can invest in environmental technologies, energy transitions, and governance systems. Implementing ESG requires financial support for initiatives like energy-saving installations, hiring consultants, or improving the work environment, which can be challenging for cash-limited SMEs.
Lack of Expertise and Technology: Effective ESG implementation requires specialized knowledge and technical skills, especially in areas such as carbon emission management, environmental protection, and data monitoring. SMEs may lack in-house experts and the funds to hire external consultants, which can hinder ESG initiatives.
Insufficient Human Resources: SMEs typically have a limited number of employees, making it difficult to dedicate a department or personnel solely to ESG projects. Employees often juggle multiple roles, limiting the time and resources available for ESG monitoring, reporting, and related tasks.
Benefits of ESG for Businesses
Risk Reduction: ESG strategies can help companies prevent and manage environmental and social risks, such as climate change, resource depletion, and labor rights issues. By prioritizing ESG, businesses are better positioned to address risks related to regulations, environmental pressures, and social demands, thereby reducing fines and legal disputes.
Enhanced Brand Image and Reputation: As consumers and investors increasingly value ESG, companies committed to it often achieve a stronger brand image, gaining consumer trust and standing out in competitive markets. For instance, environmentally friendly brands attract consumers with strong eco-consciousness.
Increased Employee Satisfaction and Productivity: ESG strategies often involve improvements to employee welfare and workplace conditions, making it easier to attract and retain talent. When employees feel aligned with the company’s social responsibility and sustainability efforts, they are more likely to embrace the company’s values, enhancing engagement and productivity.
Meeting Stakeholder Expectations: Customers, employees, communities, and suppliers are increasingly interested in a company’s ESG commitments. By strengthening ESG performance, companies can better meet these stakeholders’ expectations, building trust and facilitating stronger collaborations.
Long-Term Competitiveness and Financial Performance: Research indicates that strong ESG performance can lead to more stable financial returns. ESG strategies reduce risk, improve operational efficiency, and foster brand loyalty, thereby laying a solid foundation for long-term growth. For shareholders, good ESG performance implies more stable investment returns.
※Research Source: Impact of ESG Ratings on Financial Stability: Empirical Evidence in the Financial and Insurance Industries
Conclusion
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) serves as a critical assessment framework for sustainable business practices, helping companies enhance their competitiveness in terms of environmental protection, social responsibility, and governance. By adopting ESG practices, companies not only comply with regulatory requirements and improve their reputation but also strengthen risk resilience and build trust, creating long-term value for stakeholders. As global interest in sustainable development grows, ESG has become a key indicator of responsible and successful business operations.
Honway specializes in physical polishing, superhard abrasives, and rare earth materials, committed to providing polishing solutions with lower environmental impact. If you have any related needs or want to learn more, please feel free to contact us! Let’s work together for a sustainable future.
We offer customized adjustments to the grinding process, tailored to meet processing requirements for maximum efficiency.
After reading the content, if you still don’t know how to select the most suitable option,
Feel free to contact us and we will have specialist available to answer your questions.
If you need customized quotations, you’re also welcome to contact us.
Customer Service Hours: Monday to Friday 09:00~18:00 (GMT+8)
Phone: +8867 223 1058
If you have any topics you want to learn more about or if you find it difficult to explain over the phone, feel free to message us on Facebook.
Honway Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/honwaygroup

