Both dry and wet grinding are widely used in material processing and surface treatment, applicable to various materials such as metals, stone, and wood. Dry grinding operates without water or other coolants, while wet grinding utilizes water or cooling liquids to reduce friction and heat. Each method has its pros and cons regarding usage scenarios, efficiency, environmental impact, and costs, making it crucial to select the appropriate method for specific applications.
This article will explore the main differences between dry and wet grinding, analyze their advantages and disadvantages, highlight the tools used, and discuss their applicability to various materials to provide a reference for selection.
Table of Contents
What is Dry Grinding?
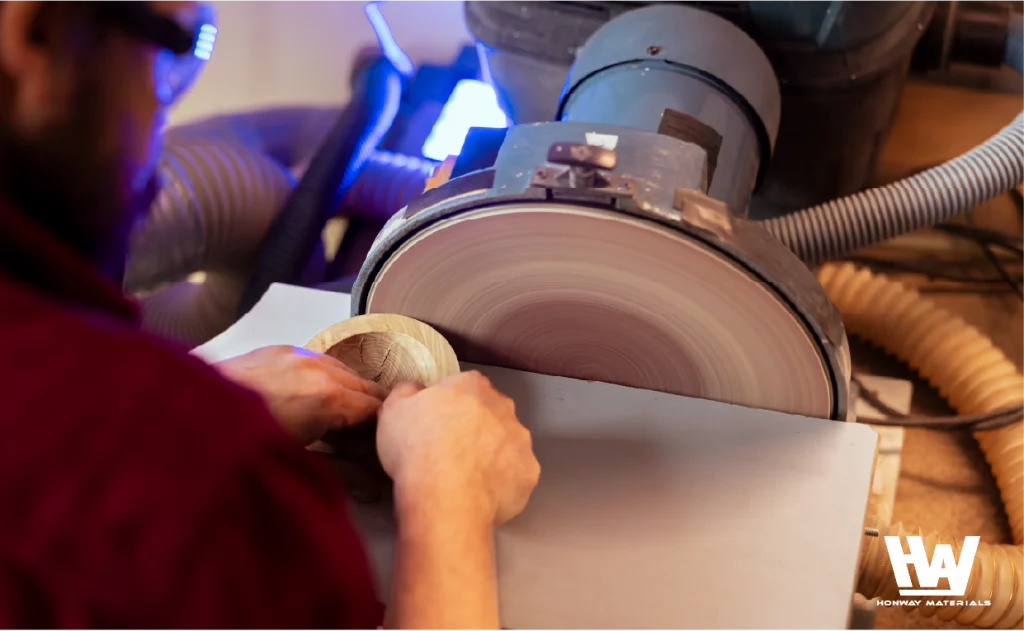

Dry grinding does not use liquids such as water or oil for cooling or lubrication. It involves direct contact between hard abrasives and workpieces to perform grinding, polishing, or leveling. Common tools used include sandpaper, grinding wheels, or diamond tools.
(Further reading: What is Dry Grinding?)
What is Wet Grinding?
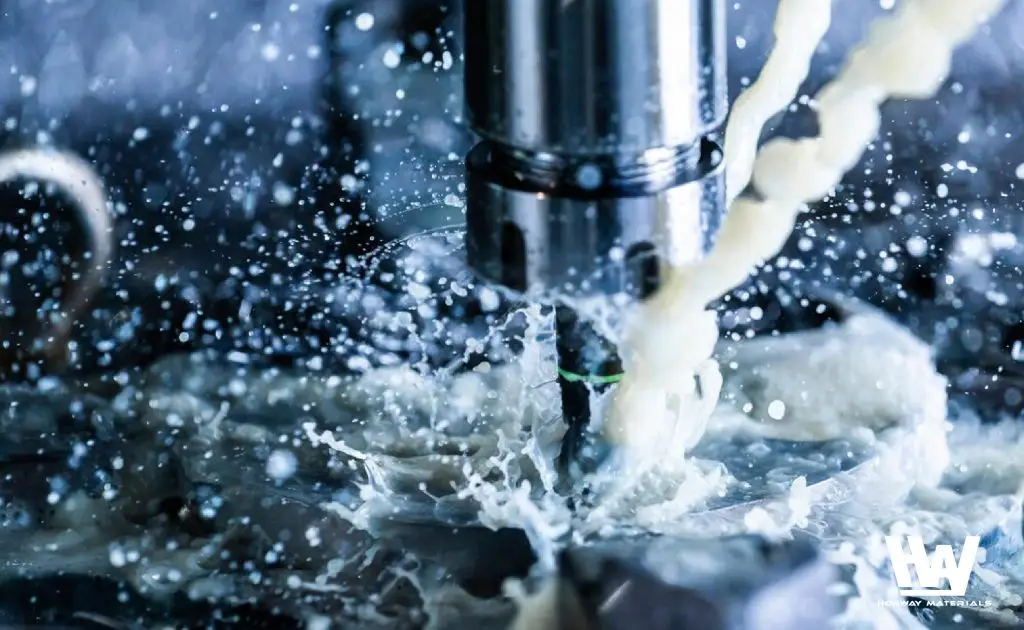

Wet grinding is a method that uses liquid as a lubricant and cooling medium. Common liquids include water, polishing solutions, alcohol, oil, or specialized solutions. Compared to dry grinding, the primary advantage of wet grinding is its ability to produce finer and more uniform particle sizes. This is due to the lubricating effect of the liquid medium, which helps reduce friction and heat generation during the grinding process. Additionally, wet grinding can enhance the dispersion and uniformity of components, thereby improving product quality and performance.
(Further reading: What is Wet Grinding?)
Comparison of the advantages of dry grinding vs wet grinding
Dry grinding and wet grinding each have their strengths and weaknesses, catering to different processing needs and material characteristics.
| Dry grinding | Wet Grinding | |
| Cost | Lower costs as it does not require cooling liquids, avoiding expenses for liquid recovery and treatment. | Higher costs due to the need for equipment and cooling liquids. |
| Operational flexibility | Can be performed anytime and is not restricted by environmental conditions, making it ideal for on-site work or scenarios where liquids cannot be used. | Requires additional cooling liquid supply systems and drainage equipment, increasing operational and maintenance costs. |
| Dust generation | Generates a significant amount of dust, posing potential risks to the environment and operator health. Dust extraction systems or protective gear are required. | Liquids suppress dust, creating a cleaner working environment and being more operator-friendly. |
| Thermal energy control | Lack of cooling results in friction generating high temperatures, potentially causing tools to overheat or material surfaces to deform. | Liquids dissipate the heat generated during processing, effectively preventing workpiece deformation, annealing, or surface damage due to high temperatures. |
| Lifespan | Due to high temperatures and friction, the lifespan of grinding tools is relatively short. | Cooling liquids reduce high-temperature wear on tools, enhancing their durability. |
| Applicable materials | Suitable for materials sensitive to chemicals or water. Ideal for scenarios where coolant contamination is undesirable, such as precision machinery or molds. | Best for materials that are heat-sensitive, high-hardness, or require precision processing. |
| Friendly environment | Dry grinding easily produces a large amount of dust and can easily cause dust pollution. Good ventilation or vacuuming is therefore required to protect worker health. | Waste liquid may pollute the environment and needs to be disposed of properly. And the recovery and treatment of coolant requires more time and resources, especially in high-volume production. |
When to apply dry and wet grinding materials
For different materials, the choice of dry grinding and wet grinding should consider material characteristics, processing effects and heat resistance.
| Dry grinding | Wet Grinding | |
| Wood | Suitable for rough grinding, shaping and surface treatment. | Not used |
| Metal | Suitable for processing soft metals such as aluminum, copper, etc., for deburring, surface roughing or rapid cutting | Suitable for processing hard metals such as stainless steel, tungsten steel, etc., for precision machining and polishing. |
| Stone (marble, granite) | Rough grinding, quick cuts or shaping. | Fine polish and surface treatment. |
| Ceramics and Glass | Initial trimming or corner removal. | Finely cut and polished to reduce cracks and scratches. |
| Plastic | Deburring or surface finishing. | Not used |
| Composite materials (carbon fiber, fiber glass) | Rough machining or shaping. | Meticulous sanding and polishing to reduce material delamination or cracks. |
| Electronics and Semiconductors | It is often used in the manufacturing of chips, micro-electromechanical systems and semiconductor components. The components require smooth surfaces and no pollution. | It is often used in heat-sensitive materials such as silicon-based materials, sapphire substrates, etc. Because stress easily occurs at high temperatures, liquid is required to reduce heat energy. |
Corresponding tools for dry and wet grinding
Dry grinding:
Diamond grinding wheel, boron nitride grinding wheel: suitable for grinding and shaping hard materials such as metal, stone, ceramics, etc.
Sandpaper (dry sandpaper): Used for sanding wood, plastic or metal surfaces, convenient and affordable.
Jet polishing machine: used for precision machining of the back end.
Diamond (silicon carbide) brush: can process irregularly shaped workpieces, used in harsh acid and alkali environments, resistant to high temperatures up to 270 degrees, and anti-static.
Angle grinder: Used with dry grinding wheels for cutting and grinding steel and stone.
Belt Sander: Commonly used in wood processing to quickly remove surface material.
Wet grinding:
Polishing pad: A soft pad installed on a polishing machine to improve the grinding or polishing effect. It is often used in conjunction with polishing fluid.
Grinding disc: Made of diamond, alumina, silicon carbide and other materials, used for material surface grinding, front-end polishing, trimming or burr removal.
Nano diamond polishing fluid: used with metallographic polishing pads for polishing.
Aluminum oxide (cerium) polishing fluid: final polishing of various metals, precision molds, sapphires, aluminum alloys, ceramics, etc., generally used for surface cleaning after diamond fluid.
Water sandpaper: Especially suitable for car polishing and detailed sanding of metal or plastic.
Wet grinding and polishing machine: used for polishing and dressing the surface of marble, granite and other stone materials.
Water jet cutting machine: uses high-pressure water flow combined with abrasives to cut materials, suitable for stone, glass and other materials.
Recommended Grinding Tools
Dry grinding
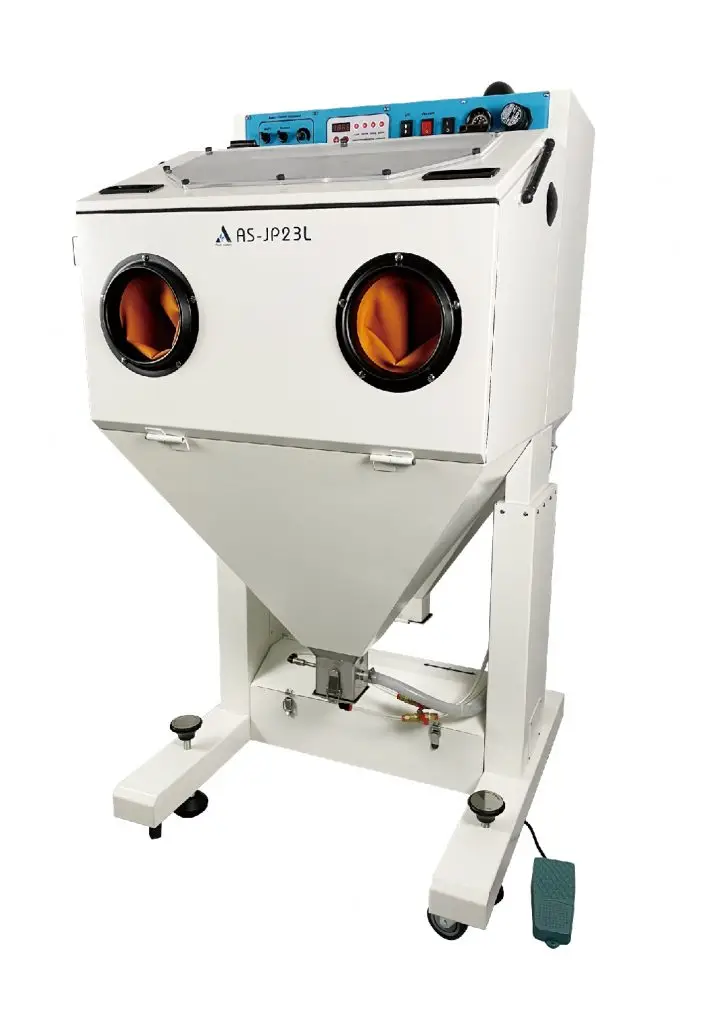
Jet Polishing Equipment >>>Jet Polishing Equipment
- The specialty of Honway lies in our use in precision machining of the back end.
- Honway utilizes flexible abrasives (multi-porous, self-adhesive grinding materials) for deburring precision parts.
- Features: Minimal grinding removal, prevents edge collapse.
- Suitable for curved surfaces, stepped areas, and grooves.
- Quickly set up spray-polishing processing times.
- Simple and quick changeover for all types of sandblasted materials: coarse, medium, fine and glossy.
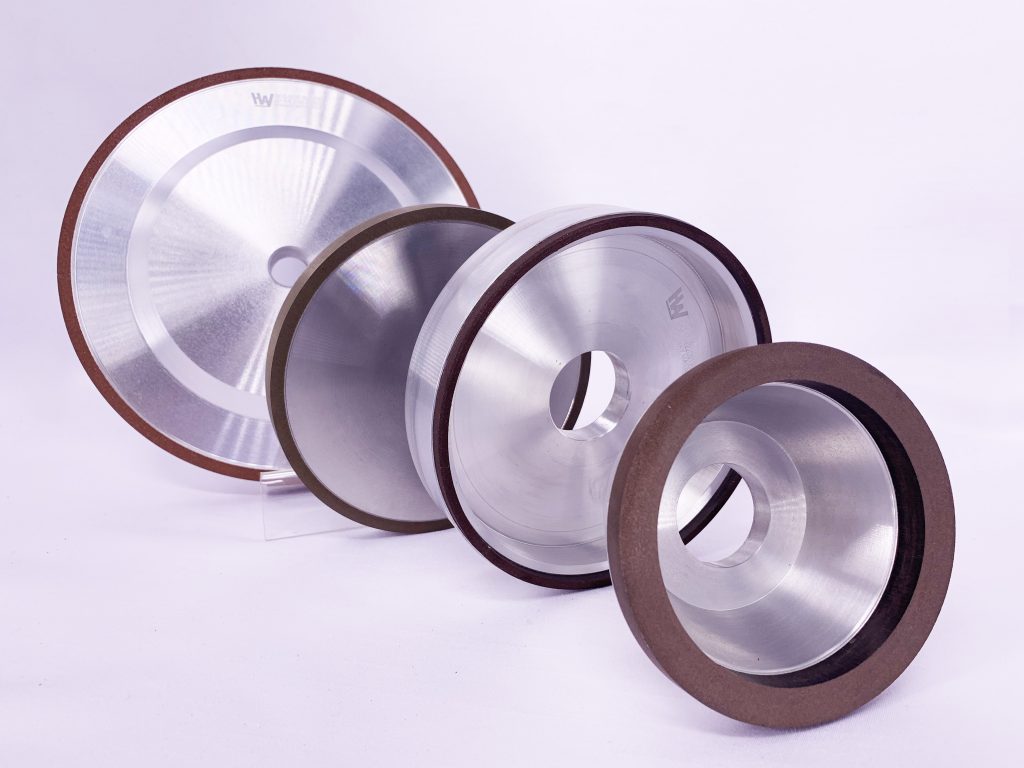
Diamond and Boron Nitride Grinding Wheel >>>Diamond and Boron Nitride Grinding Wheel
- Abrasive Types: Natural diamond, synthetic diamond, synthetic metal-coated diamond, boron nitride, metal-coated boron nitride.
- Binders: Resin, ceramic, metal, electroplating.
- Cooling Methods: Dry grinding, wet grinding.
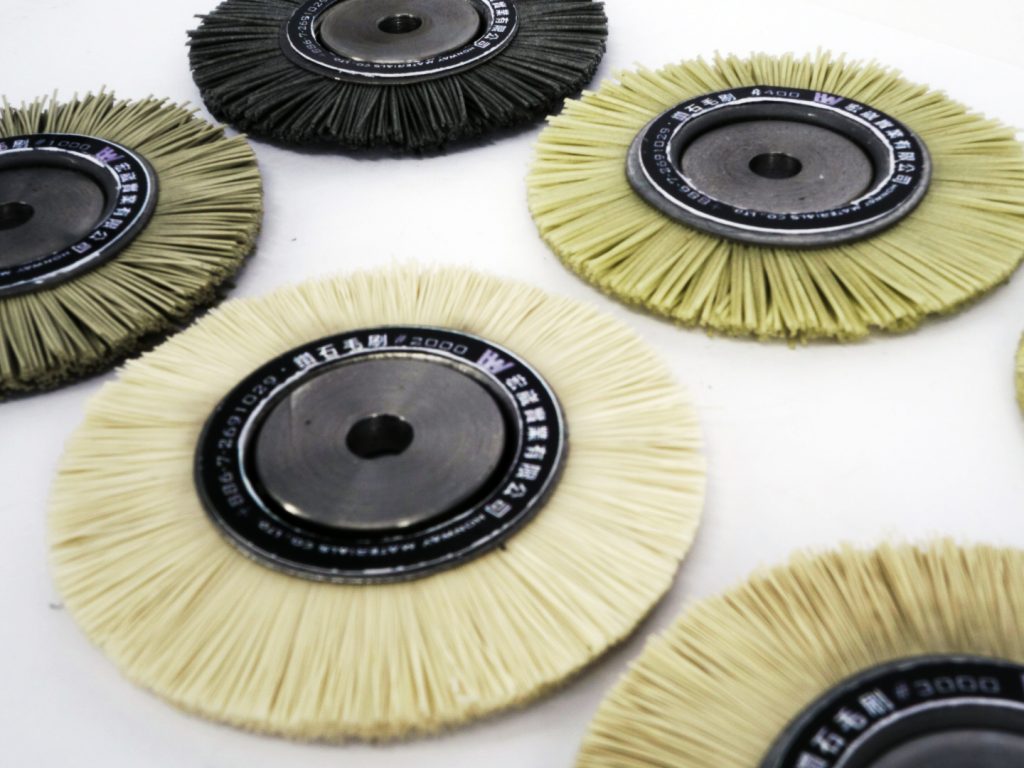
Diamond Brush >>>Diamond Brush
- Processes irregularly shaped workpieces.
- Features: Resistant to harsh acidic or alkaline environments, withstands temperatures up to 270°C, and is anti-static.
- Applications: Hard alloys such as titanium carbide and tungsten carbide, sapphire glass and general glass processing.
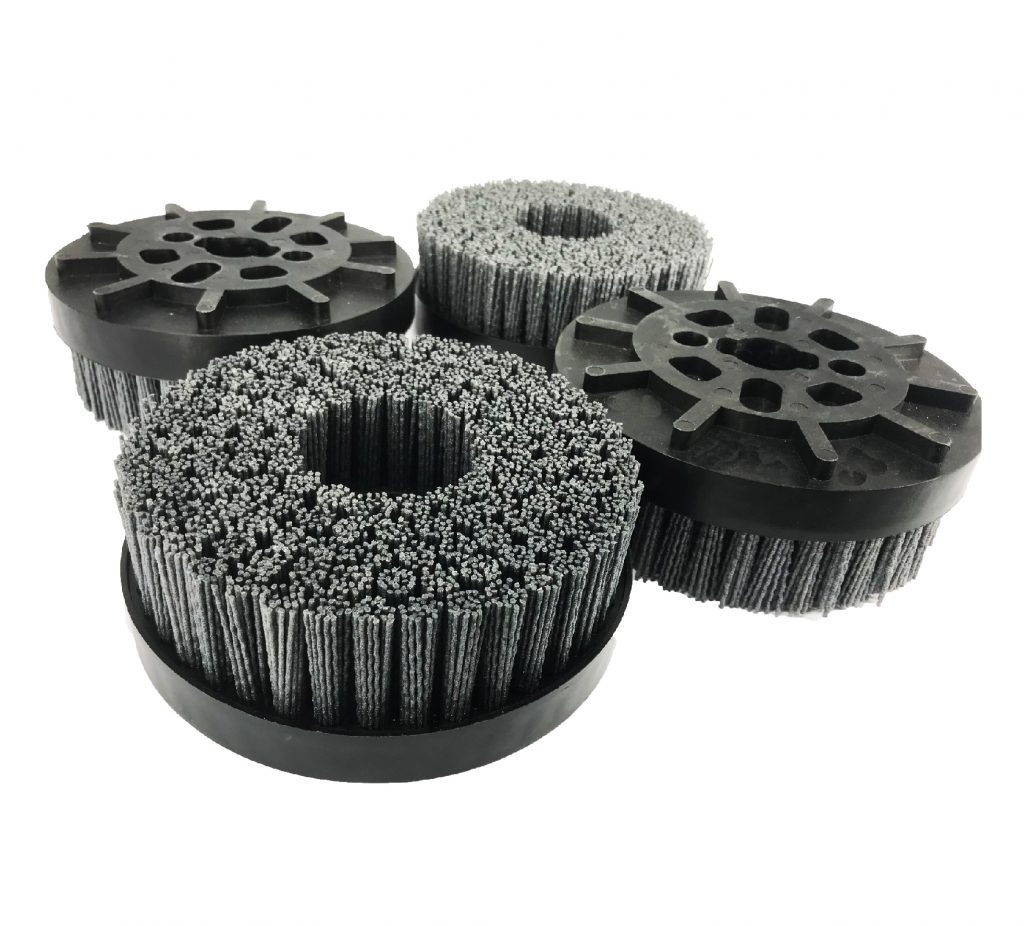
Silicon Carbide Brush >>>Diamond Brush
- Workpieces can be directly reprocessed after cutting.
- Stable and repeatable results are achieved through the continuous release of abrasive particles.
- Shape stability and high precision ensure process safety.
Wet Grinding
Nano diamond polishing solution / Grinding solution / Suspension >>>Polishiing solution
- Best suited for: mechanical operation
- State: liquid (oil-based/water-based/alcohol-based)
- Polishing can be performed using a double-sided grinding machine, chemical mechanical polishing (CMP), or metallographic grinding.
- ※ Since the abrasive is in a free state, it is suitable for large-scale polishing.
- ※ If the surface of the workpiece is still rough, choose a polishing liquid with larger particles.
Alumina / Cerium oxide polishing solution / Grinding solution / Suspension >>> Polishing solution
- Best suited for: mechanical operation
- Status: Liquid
- Scope of application: Generally used after diamond compound
- ※ Possesses the ability of repairing polishing marks on the workpiece.
- ※ Cerium oxide is recommended to be used with tools at low speed.
Polishing pad / Grinding pad >>>> Metallographic consumables
- Materials:
- Contains abrasive: Cerium oxide polishing pad, Diamond resin grinding disc, Electroplate diamond grinding disc
- Without abrasives: silk, leather, polyurethane (black velvet), woven fabric, fleece, porous, hard cloth, soft cloth, etc.
Conclusion
The primary difference between dry and wet grinding lies in the use of liquids and their impact on processing results and the environment. Dry grinding does not require cooling liquids, offering simplicity in operation. It is suitable for rough machining and portable tasks but produces large amounts of dust and may lead to tool overheating. Ideal for materials like wood and plastics that are less sensitive to liquids. Wet grinding uses cooling liquids to reduce frictional heat and suppress dust. It is suitable for processes requiring high precision and smooth finishes, such as fine machining of stone and metal. However, it involves higher equipment costs and environmental handling requirements.
Choosing the appropriate method depends on processing needs, material characteristics, and the working environment. Selecting the right grinding approach can enhance operational efficiency and workpiece quality.
Action
- Common surface treatments for metal and wood>>What is Dry Grinding?, What is Wet Grinding?
- Can current polishing and processing methods be replaced with lower-carbon alternatives?>>Why is Mechanical Polishing More Environmentally Friendly than Chemical Polishing?
- How to Implement>>Diamond and Boron Nitride Grinding Wheels, Polishing Equipments, Polishing Tools, Metallographic Consumables, Grinding Slurry
- Implement testing and review
Honway focuses on the fields of physical polishing, superabrasives and rare earth raw materials, and is committed to improving processing efficiency and providing polishing solutions with lower environmental pollution for customers. If you have related needs or want to know more, please feel free to contact us! Let’s work together for a sustainable future.
Customized Grinding Solutions: We offer tailored adjustments to our grinding processes, allowing us to meet specific processing needs for maximum efficiency.
After reading the content, if you still don’t know how to select the most suitable option,
Feel free to contact us and we will have specialist available to answer your questions.
If you need customized quotations, you’re also welcome to contact us.
Customer Service Hours: Monday to Friday 09:00~18:00 (GMT+8)
Phone: +8867 223 1058
If you have a subject that you want to know or a phone call that is not clear, you are welcome to send a private message to Facebook~~
Honway Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/honwaygroup