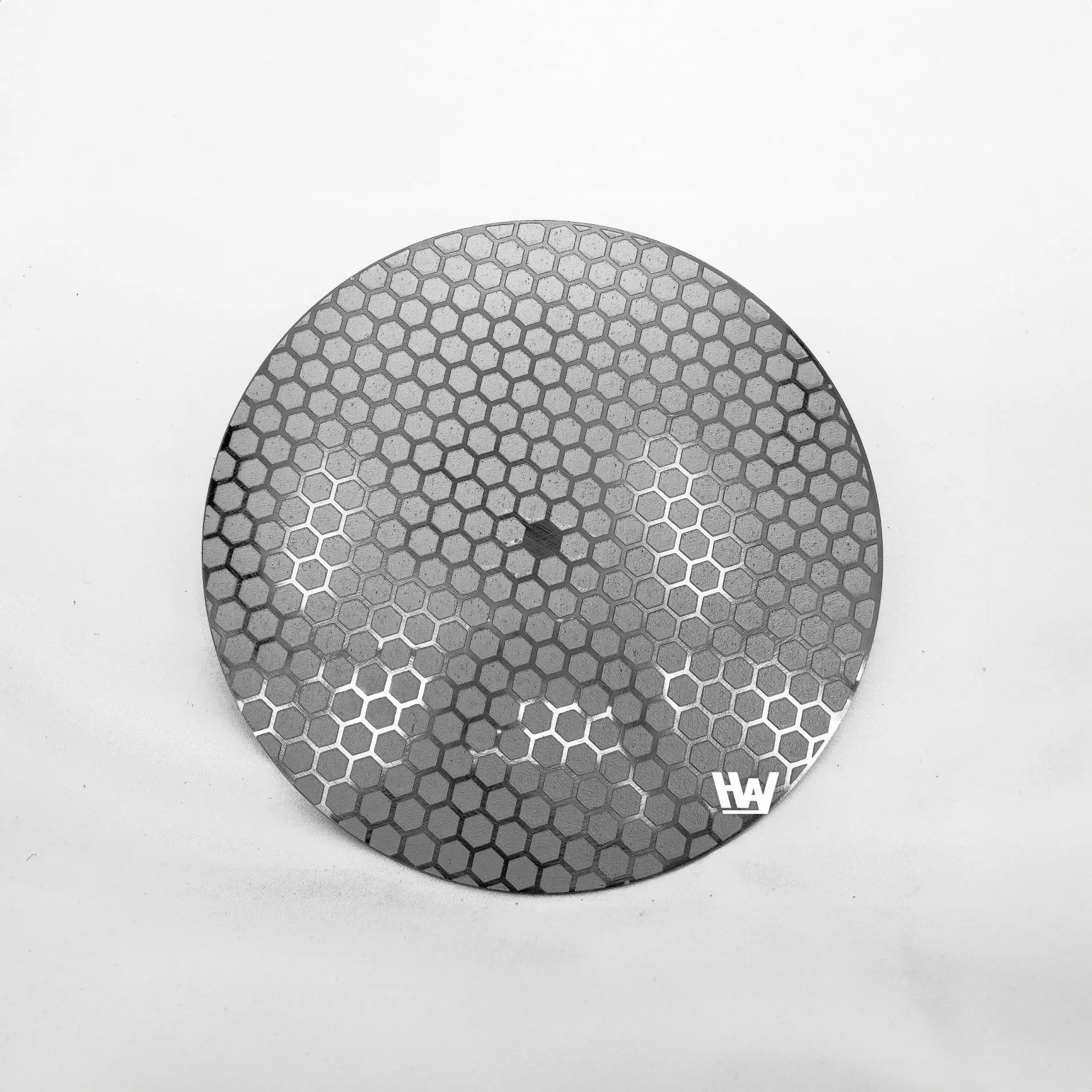
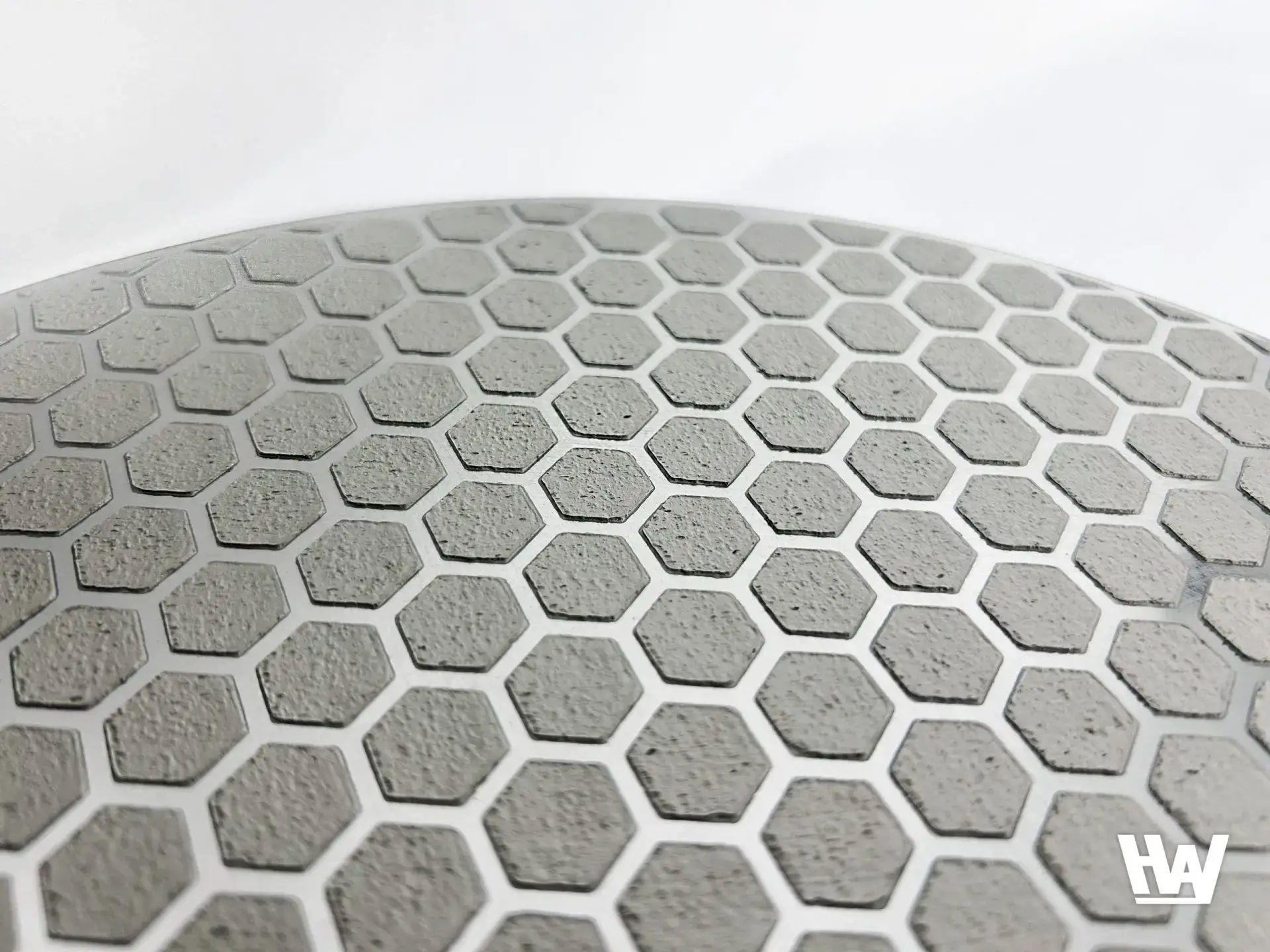
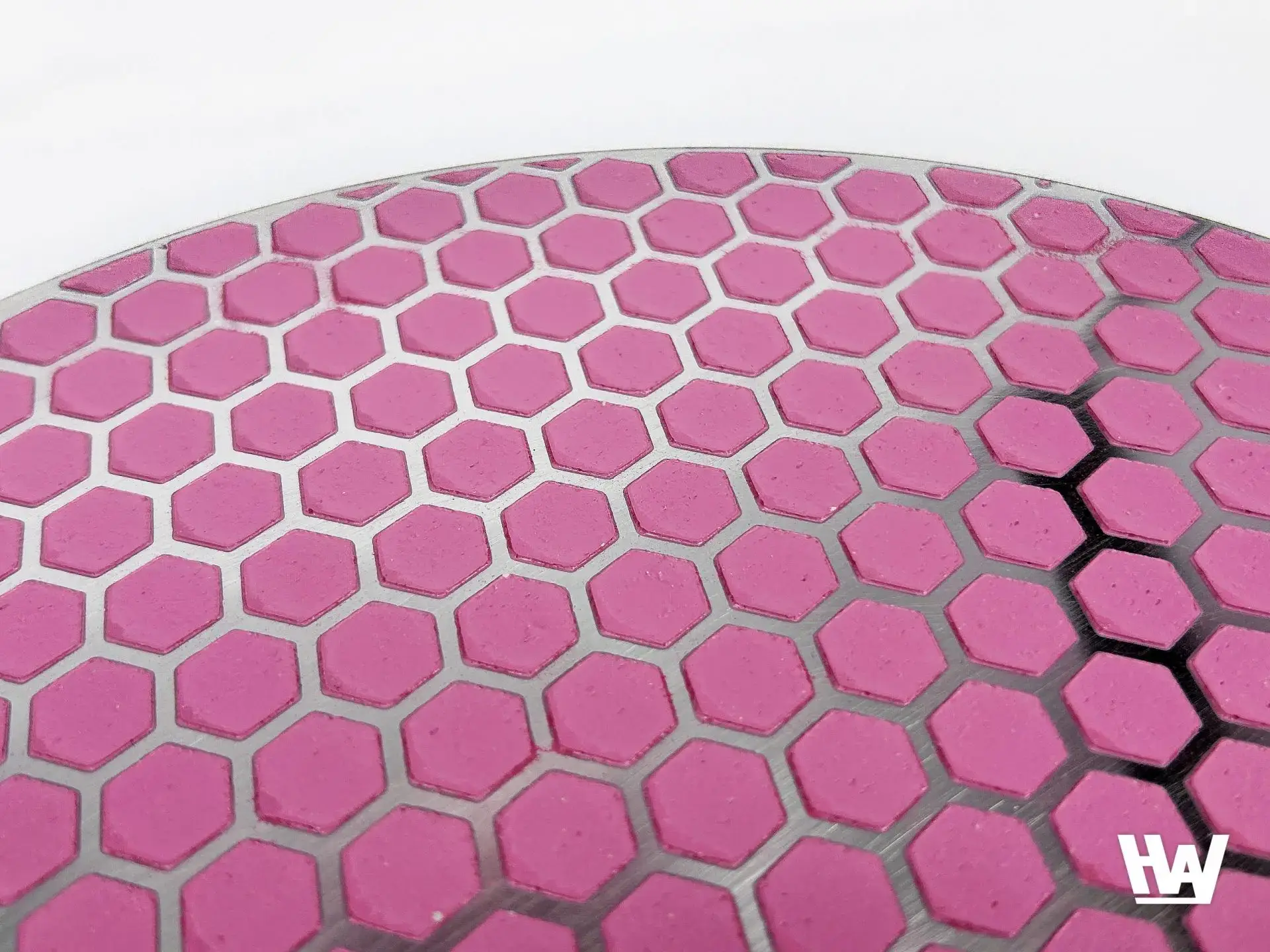
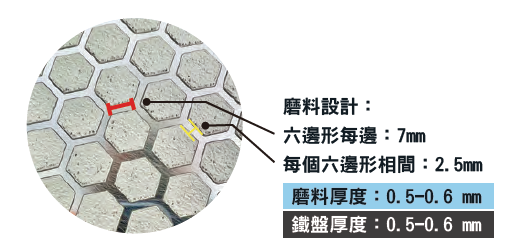
HW-Largo (Hexagonal) – Metallographic fine grinding disc Product features
☑️ Reduce process / Combined back-end grinding and front-end polishing, enhancing work efficiency.
☑️ Highly efficient / Flexible backing plus high quality abrasives, small residual scratch on the cut surface, improving subsequent polishing quality.
☑️ Widely applicable / Soft fine grinding discs are available with different abrasive types and grit sizes, suitable for workpieces of varying hardness.
☑️ High Flatness / Uniformly fine grinds both soft and hard materials, preventing rounding or chamfering, and ensuring sample consistency.
☑️ High Quality and Efficiency / Grid pattern reduces debris accumulation, provides consistent high removal rate, and ensures cross-sectional flatness.
Application areas:
- Materials science, metal identification, failure analysis, manufacturing, materials research and development, diamond and gemstone processing, electronics and semiconductor industries.
- Copper-clad laminates, double-sided grinders, and single-disc grinders.
Product features
|
Abrasive |
Particle size(um) | Size(mm) |
Size(in) |
| Diamond | 0.5
1.0 2.0 3.0 6.0 9.0 |
Ø127
Ø200 Ø220 Ø230 Ø250 Ø300 Ø350 Ø380
|
Ø5
Ø8 Ø8.6 Ø9 Ø9.5 Ø12 Ø14 Ø15
|
| Aluminum Oxide | |||
| Silicon carbide | |||
| Cerium Oxide | 0.5
1.0 2.0 3.0
|
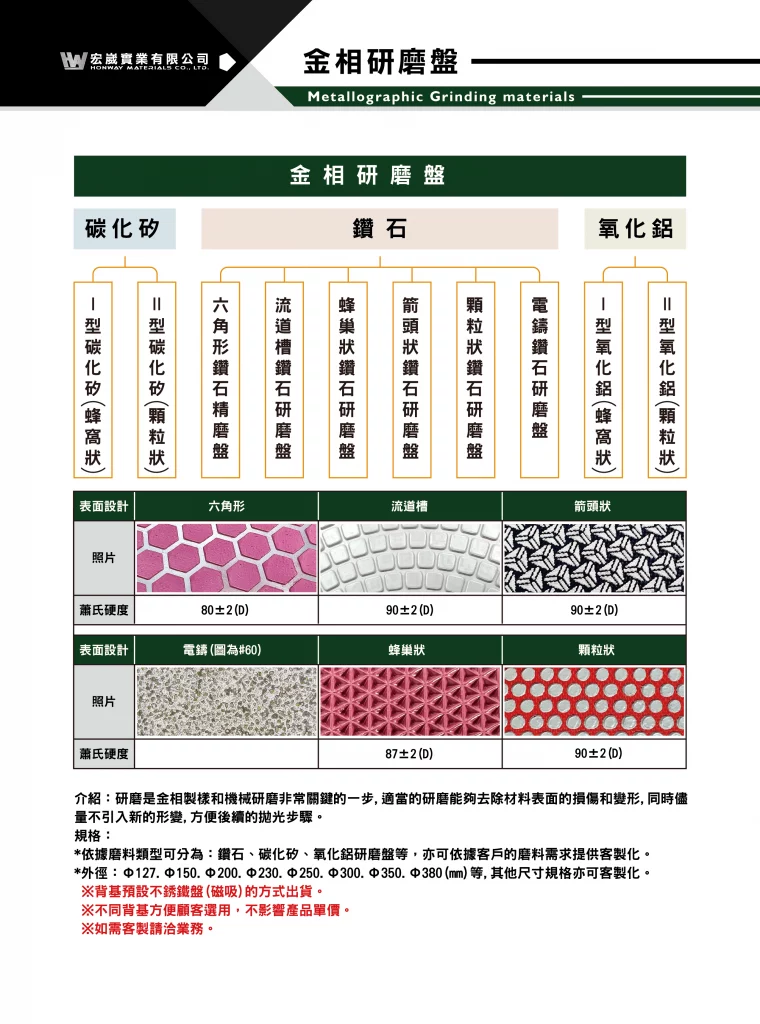
1. Product differences
| Metallographic fine grinding disc | Metallographic grinding disc | |
| Abrasive layer | soft | hard |
| Shore hardness | 80 degrees | 90 degrees |
| Introduction | Soft as cowhide | Hard as steel |
| Application | Replaces the three processes of back-end grinding and front-end polishing | Replaces sandpaper for grinding super-hard materials |
2. How to Choose
How to choose abrasives: The specific application depends on the hardness of the workpiece material and your current actual process. like:
- Diamond: super cemented carbide, electronic materials, ceramics.
- Aluminum oxide: soft metal, plastic, glass, IC substrate, packaging materials, semiconductors and various electronic parts, printed circuit boards (PCB) and connectors.
- Silicon Carbide (SiC): Suitable for semiconductor materials (such as silicon wafers and gallium arsenide), electronic materials, superhard metals, ceramics, glass, and gemstones.
- Cerium Oxide (CeO₂): Used for optical glass (lenses, prisms, and other optical components), gemstones, ceramics, semiconductors (such as wafers), and cubic zirconia.
(Note: The above applications are for reference only. The specific use should depend on the hardness of the workpiece material and your current process requirements.)
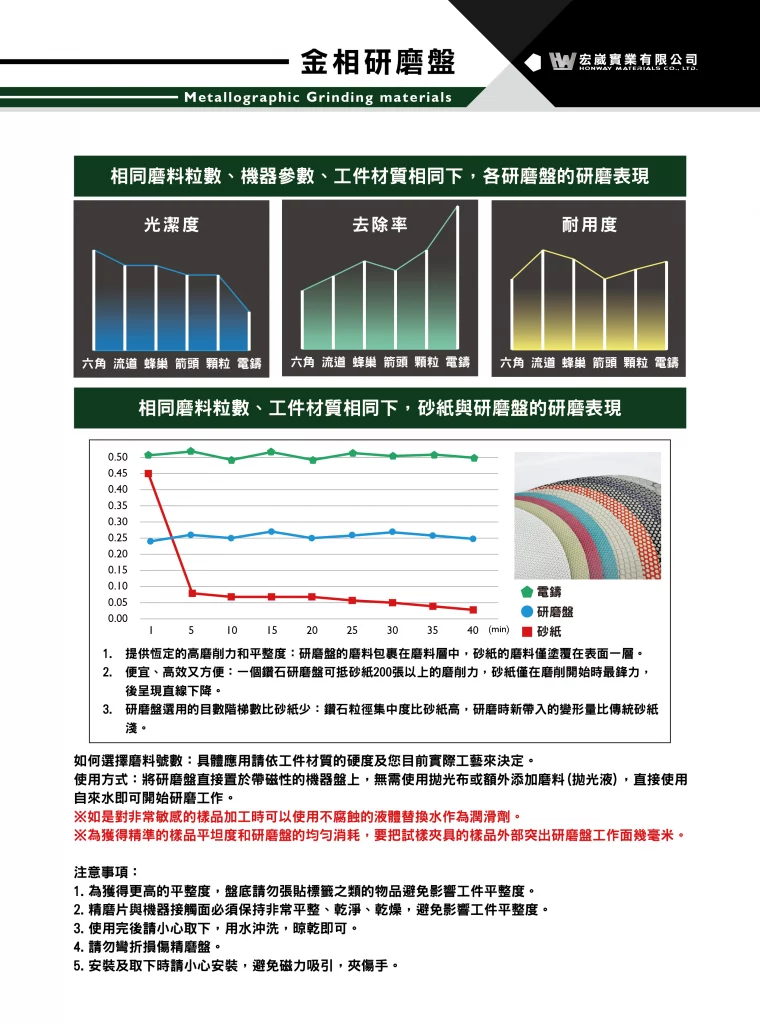
Grit size selection: The 3.0um (4000#) fine grinding disk facilitates a seamless progression from a preceding 6.0um (2400#) grinding stage to a subsequent 1.0um polishing stage, followed by a final, precision polishing step using a polishing cloth devoid of polishing slurry.
Usage instructions: Simply place the fine grinding disc directly onto the magnetic machine plate. No polishing cloth or additional abrasives (polishing liquid) are needed; you can begin fine grinding using tap water.
3. Precautions
- For optimal flatness, avoid sticking any labels or similar items to the bottom of the disc to prevent affecting workpiece flatness.
- Ensure that the contact surface between the grinding disc and the machine is very flat, clean, and dry to avoid impacting the workpiece’s flatness.
- After use, carefully remove the pad, rinse with water, and let it air dry.
- Avoid bending or damaging the precision grinding disc.
- When installing or removing, do so carefully to avoid magnetic attraction pinching your hands.