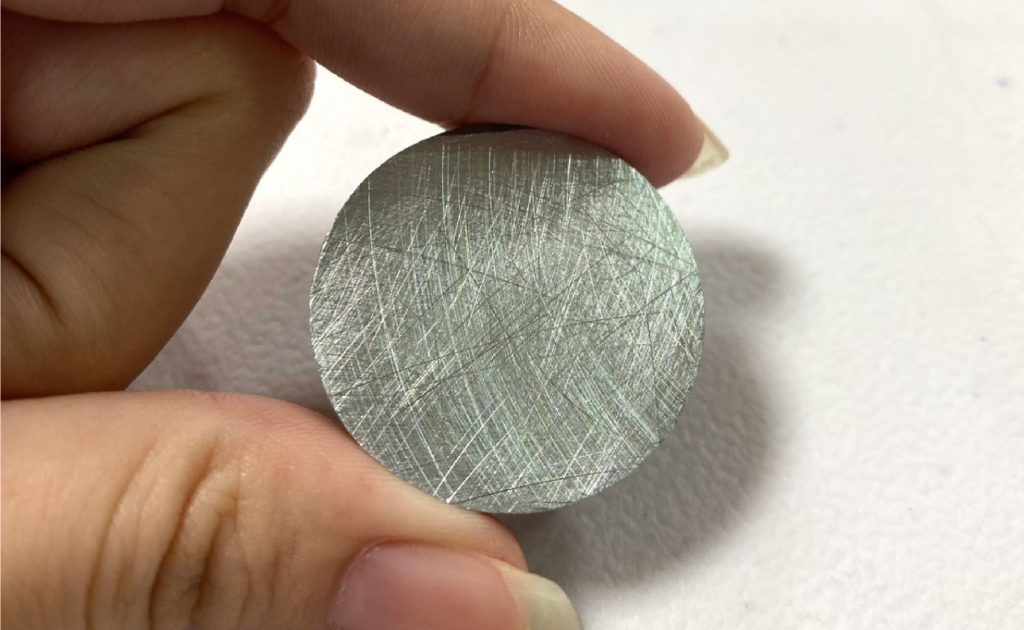
Science Classroom
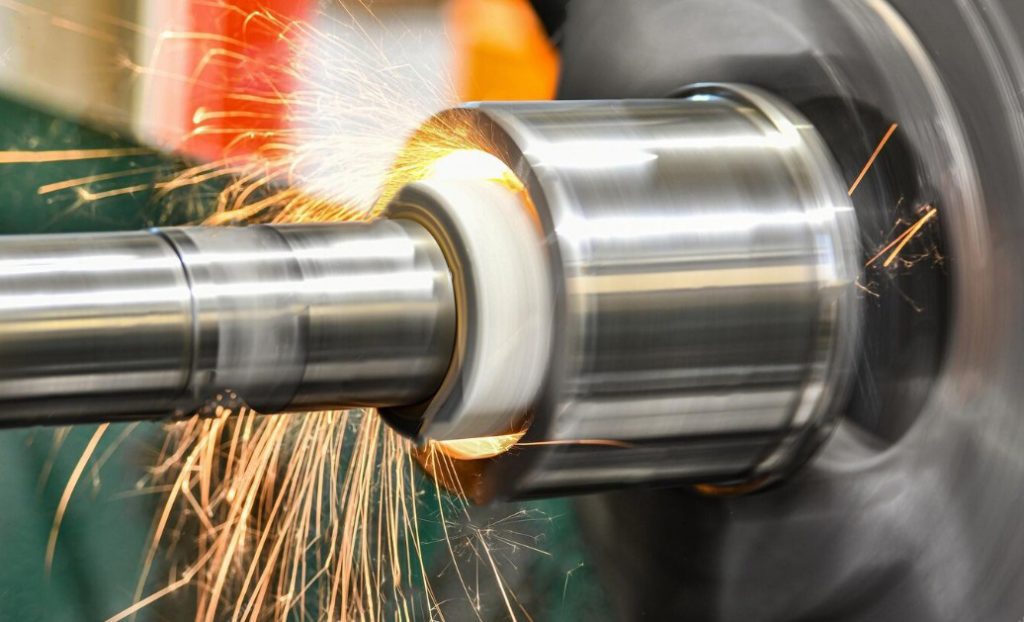
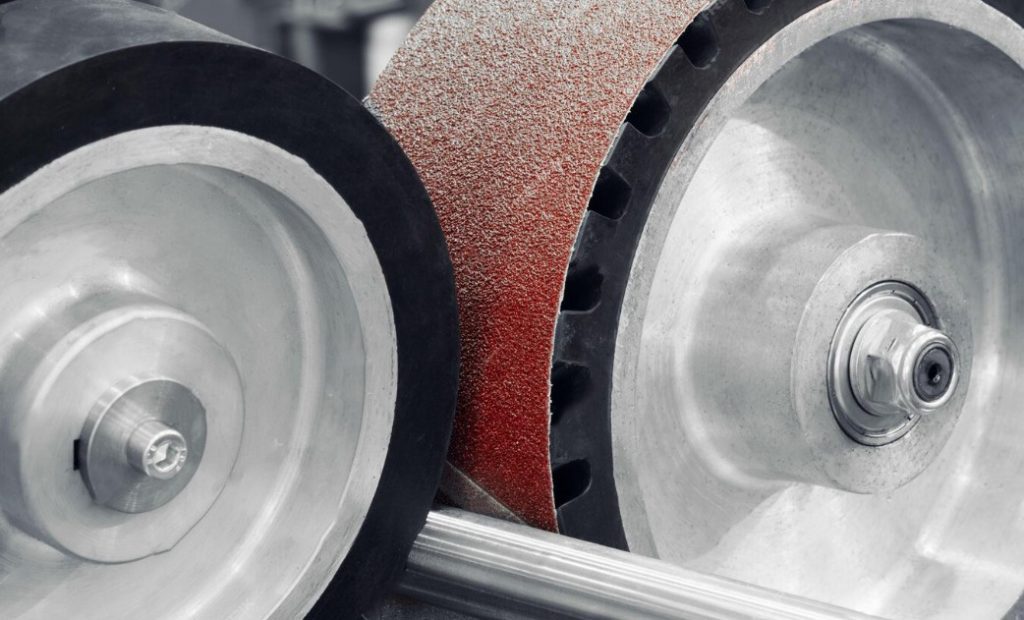
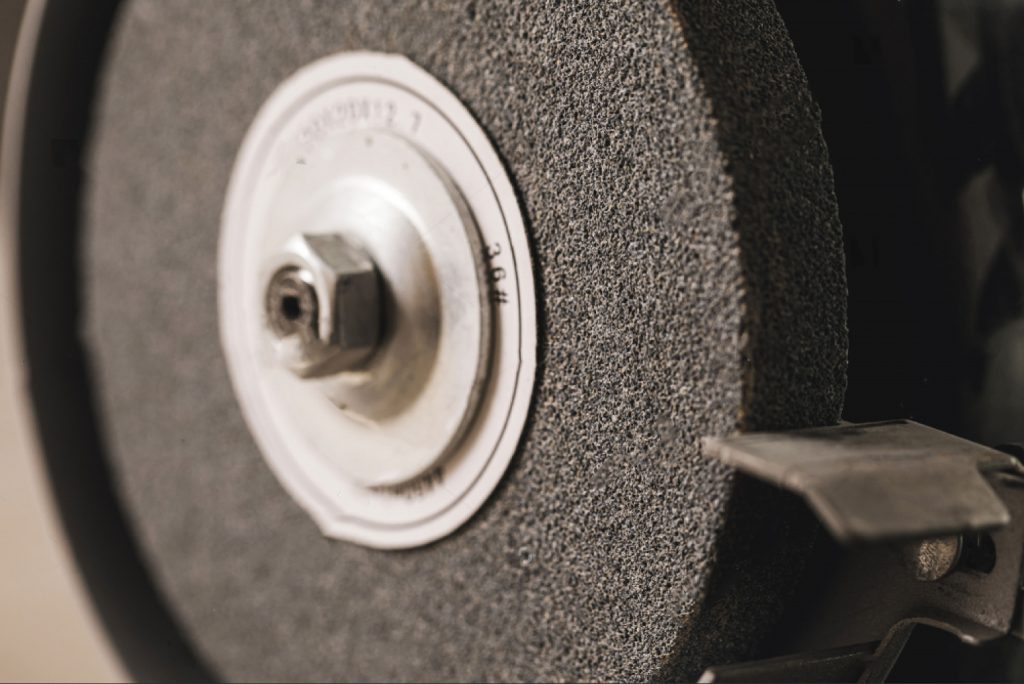
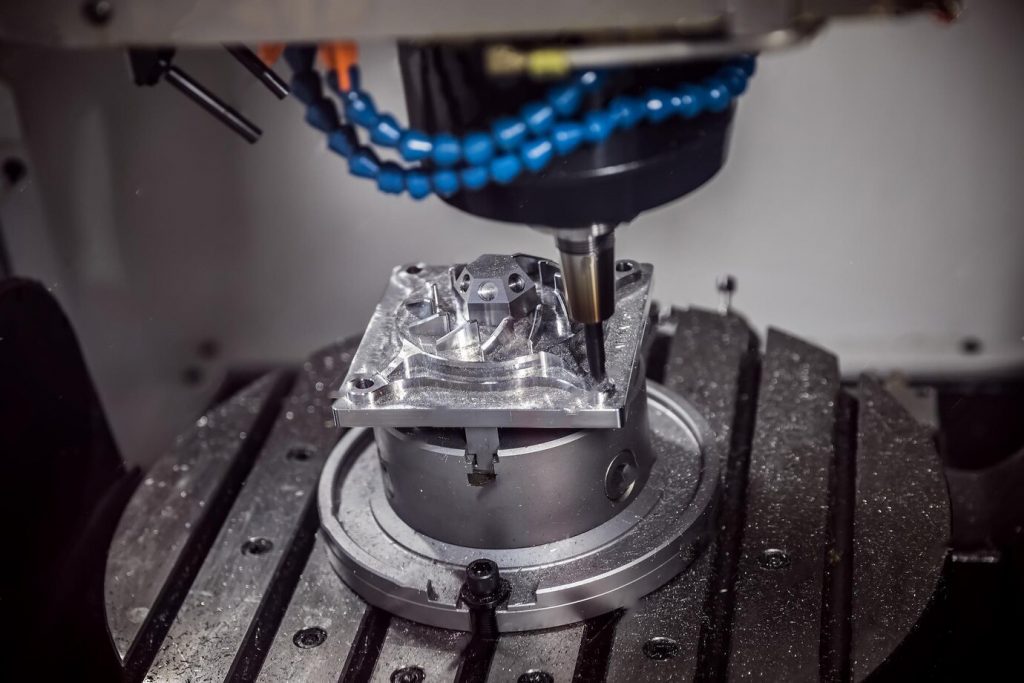
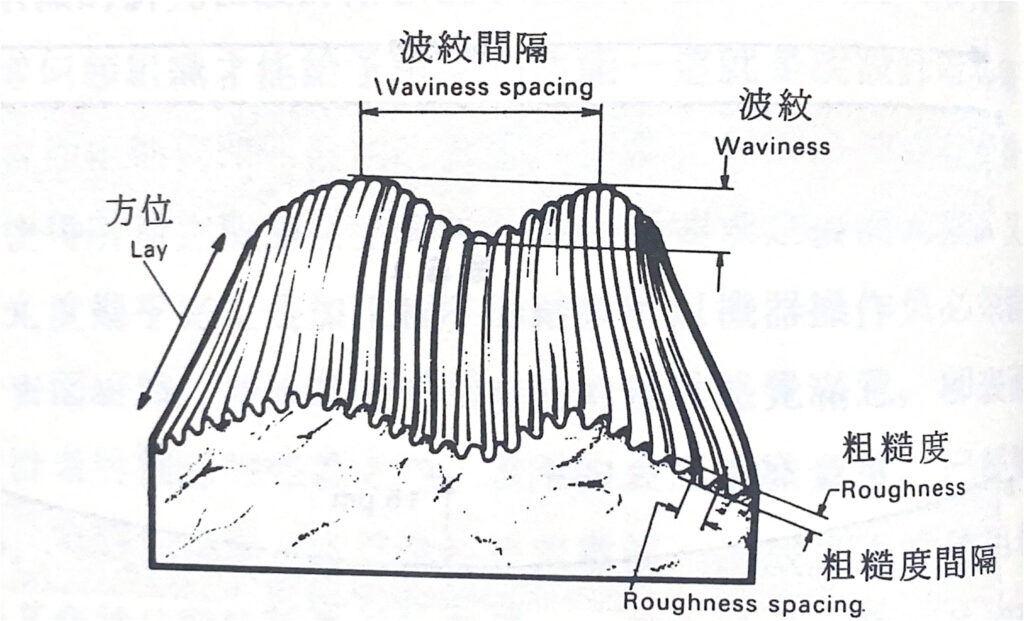
Science Classroom : Do you have machining problems? Do your workpieces always have pitting and orange peel? Do you want to know the application of nanotechnology? Here we have a series of industrial science tips to share with you! If you have any questions, please contact us directly and we will help you to solve your problems.
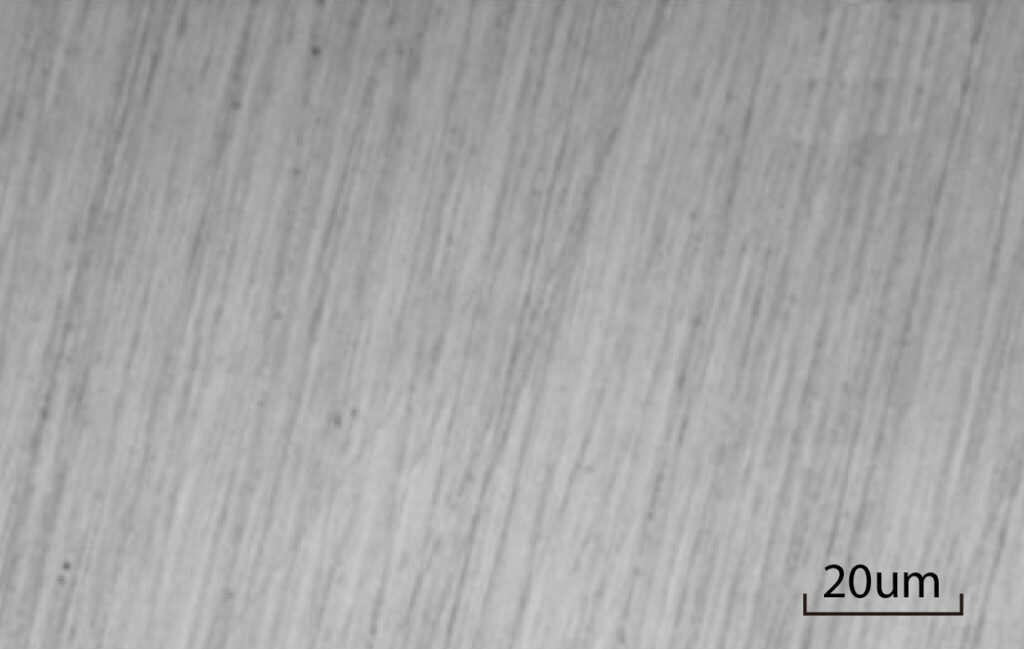




-1024x689.jpeg)