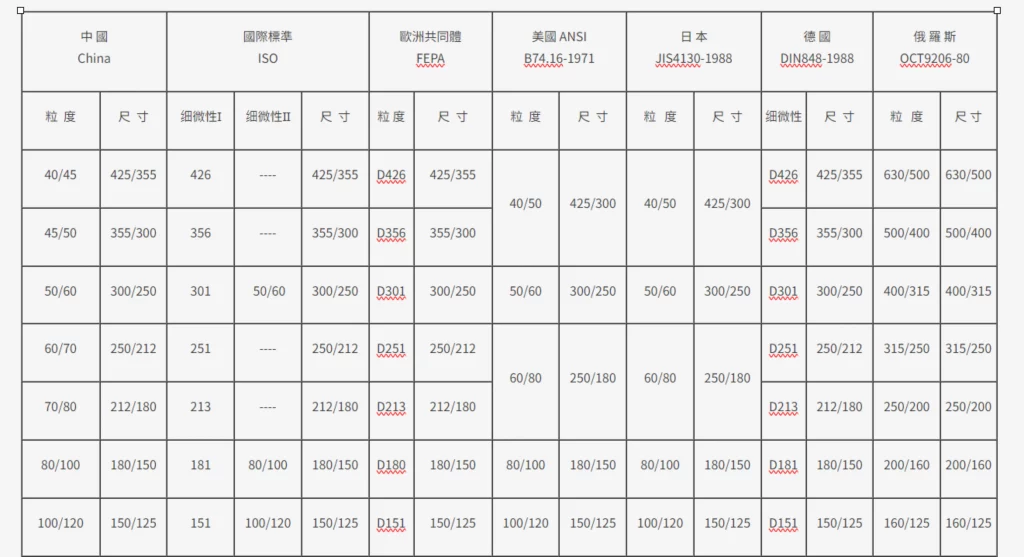
Diamond Knowledge
Diamond Knowledge: Diamond is a symbol of love and an indispensable element in industry. Diamond is one of the top five precious stones, do you know enough about it? Let Honway take you through all aspects of the diamond, from how it is created to how to select it!